Image:The Normal DDAH Mechanism.jpg
From Proteopedia
Size of this preview: 800 × 413 pixels
Full resolution (1215 × 627 pixel, file size: 65 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
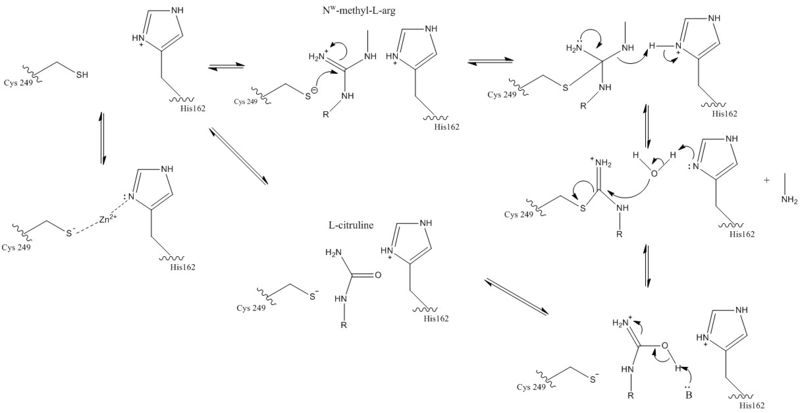
The normal mechanism of DDAH. This figure highlights the importance of Cys249 acting as the nucleophile that attacks the guanidinium carbon on the substrate that is held in the active site via hydrogen bonds. The tetrahedral product collapses as the alkylamine leaving group leaves. The sp2 thiouronium intermediate is hydrolyzed to form citrulline. His162 protonates the alkylamine leaving group and generates hydroxide to hydrolyze the intermediate formed in the reaction.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | User | Dimensions | File size | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (current) | 00:41, 31 March 2017 | Natalie Van Ochten (Talk | contribs) | 1215×627 | 65 KB | The normal mechanism of DDAH. This figure highlights the importance of Cys249 acting as the nucleophile that attacks the guanidinium carbon on the substrate that is held in the active site via hydrogen bonds. The tetrahedral product collapses as the alkyl |
- Edit this file using an external application
See the setup instructions for more information.
Links
The following pages link to this file:
