Trypsin
From Proteopedia
FunctionTrypsin or serine protease 1 is a medium size globular protein that functions as a pancreatic serine protease. This enzyme hydrolyzes bonds by cleaving peptides on the C-terminal side of the amino acid residues lysine and arginine. It has also been shown that cleavage will not occur if there is a proline residue on the carboxyl side of the cleavage site. Trypsin was first discovered in 1876 by Kuhne, who investigated the proteolytic activity of the enzyme. In 1931 the enzyme was purified by crystallization by Norothrop and Kunitz and later in 1974 the three dimensional structure of trypsin was determined. Throughout the 1990's the role of trypsin in hereditary pancreatitis and the mutation that causes it was discovered. Today trypsin is used in the development of cell and tissue protocols, as well as in the medical field to determine the role of trypsin in pancreatic diseases[1].
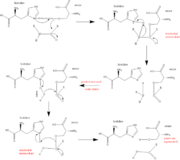
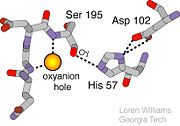
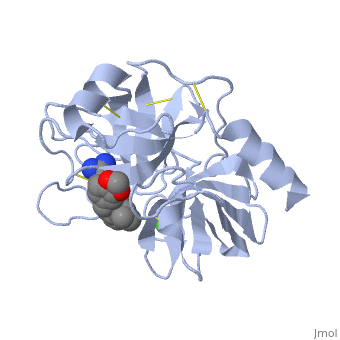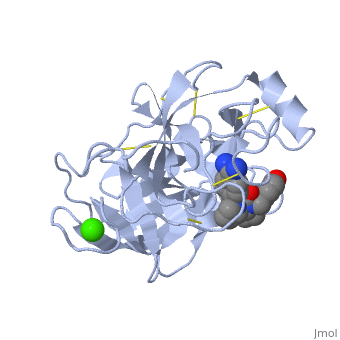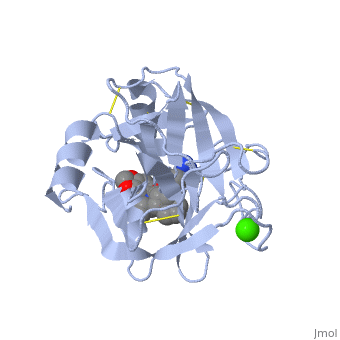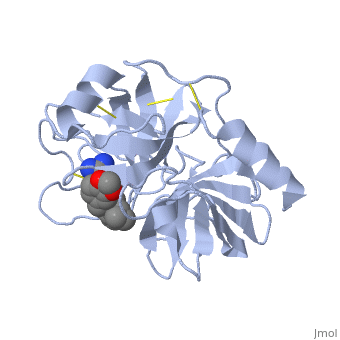
Trypsin has many applications due to fact that it is easily purified in high quantities. The trypsin enzyme is often used in the research setting to digest proteins and then identify the resulting peptides using mass spectrometry. Trypsin has many uses in the medical field such as dissolving blood clots and treating inflammation. Other applications include its use in pre-digesting of baby food, fingerprinting and sequencing work, and environmental monitoring [3]. For additional details see Ligand Binding and CatalysisThe structure of this particular bovine trypsin was determined in complex with UB-THR 10, formula C20H29N5O2, along with two sulfate ions (highlighted) and a calcium ion (green). Four key amino acids interact with calcium at a subsite loop. The binding of ligand UB-THR 10 involves water bridges, direct hydrogen bonding, and a host of hydrophobic interactions. The figure below shows this binding in two dimensions. The binding of trypsin to UB-THR 10 somewhat emulates the binding to its specific peptide substrates. The preference for lysine or arginine in trypsin catalysis is due to the composition of the trypsin specificity pocket. Here (green), Asp 189 and one of two significant glycine backbones, Gly 216, interact with the ligand as they would with Arg or Lys. The catalytic triad; Asp 102, His 57, and Ser 195, shown here in yellow, is positioned near the substrate. The catalytically active histidine and serine side chains are even near an amide bond in UB-THR 10, just like the amide bond broken in peptide hydrolysis. According to FirstGlance in Jmol, there is no bonding of these groups with the ligand, apart from minor van der Waal's interactions with Hist 57. If Ligand UB-Thr 10 were a transition state analog, some covalent connection would exist in addition to hydrogen bonds. UB-THR 10 simulates the substrate, but does not hydrolyze at either of its two amide bonds, likely due to the local cyclic groups atypical of peptide backbones. RegulationTrypsin has long been known as unique in that it is an allosterically regulated monomer [1]. In viewing the 3D structure, the allosteric sight appears to most likely be the subsite loop, which can bind Calcium. New research involving structural comparisons of trypsin-like serine proteases bound and unbound to Calcium and other effectors is being done to better understand the mechanism of this regulation[2]. Catalytic MechanismThe function of Trypsin is to break down peptides using a hydrolysis reaction into amino acid building blocks. This mechanism is a general catalytic mechanism that all Serine proteases use. The active site where this mechanism occurs in Trypsin is composed of three amino acids and called a catalytic triad. The three catalytic residues are Serine 195, Histidine 57, and Aspartate 102 [4]. The structure of the catalytic triad and the mechanism are shown in the figures to the right. In the mechanism, serine is bonded to the imidazole ring of the histidine. When histidine accepts a proton from serine an alkoxide nucleophile is formed. This nucleophile attacks the substrate when the substrate is present. The role of the aspartate residue is hold histidine in the proper position to make it a good proton acceptor. What makes this mechanism works is that a pocket if formed from the three residues and the three residues function to hold each other in proper position for nucleophilic attack. The steps of the mechanism involve two tetrahedral intermediates and an Acyl-enzyme intermediate [5]. The mechanism can be followed in more detail in the figure on the right [6]. Oxyanion HoleAn important motif that is formed in this reaction is an oxyanion hole. This is also shown in the figure to the right [7]. This oxyanion hole is specifically formed between the amide hydrogen atoms of Serine 195 and Glycine 193. This oxyanion hole stabilizes the tetrahedral intermediate through the distribution of negative charge to the cleaved amide [8]. Trypsin-BPTI complexThe trypsin backbone is shown in pink and the trypsin inhibitor, BPTI, in yellow (PDB code 2ptc). The active site residues [Ser195-His57-Asp102-Ser214] are shown in green, the disulfide bond between residues 14-38 is shown in yellow and the Lys 15 sidechain at the specificity site in pink. See also Ann Taylor 115. Comparison to Chymotrypsin and ElastaseStructure of Chymotrypsin and Elastase. Trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase are all digestive enzymes that are produced in the pancreas and catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds. Each of these enzymes has different specificities in regards to the side chains next to the peptide bond. Chymotrypsin prefers a large hydrophobic residue, trypsin is specific for a positively charged residue, and elastase prefers a small neutral residue. Chymotrypsin, trypsin and elastase are all proteins that contain a catalytic mechanism and hydrolyze peptides using the serine protease mechanism. Chymotrypsin and elastase are both homologs of Trypsin since they are 40% alike in structure and composition [9]. In the Chymotrypsin structure shown the alpha helices are blue, the beta sheets are green, and the remainder of the protein is red. In the Elastase structure shown the alpha helices are in red, the beta sheets are yellow, and the remainder of the protein is orange.
3D structures of Trypsin
|
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Trypsin. 2010. 30 October 2010 <http://www.worthington-biochem.com/tyr/default.html>
- ↑ Trypsin. 30 October 2010 <http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/life-science/metabolomics/enzyme-explorer/analytical-enzyme/trypsin.html>.
- ↑ Trypsin. 2010. 30 October 2010 <http://www.worthington-biochem.com/tyr/default.html>
- ↑ Pratt, C.W., Voet, D., Voet, J.G. Fundamentals of Biochemistry - Life at the Molecular Level - Third Edition. Voet, Voet and Pratt, 2008.
- ↑ Structural Biochemistry. 10 June 2010. 30 October 2010.<http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Structural_Biochemistry/Enzyme/Catalytic_Triad>.
- ↑ Image From:

- ↑ Williams, Loren. Georgia Tech. http://www2.chemistry.gatech.edu/~1W26/bcourse_information/6521/protein/serine_protease/triad_1/html.
- ↑ Structural Biochemistry. 10 June 2010. 30 October 2010.<http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Structural_Biochemistry/Enzyme/Catalytic_Triad>.
- ↑ Pratt, C.W., Voet, D., Voet, J.G. Fundamentals of Biochemistry - Life at the Molecular Level - Third Edition. Voet, Voet and Pratt, 2008.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Eran Hodis, Leah Bowlin, David Canner, Karsten Theis, Glenn Jones, Ben Hallowell, Karl Oberholser, Jaime Prilusky