User:Anna-Marie Šůchová/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
Contents |
COVID-19 – current knowledge
Covid-19 is an infectious diseases that started spreading in November 2019 from China´s city Wuhan and quickly spread throughout the whole world (including separated islands like Bermuda island). The disease is caused by novel coronavirus SARS-Cov2. In some cases the disease results in severe pneumonia, organ failure or cytokine storm leading to overall exhaustion of the immune system and death.
Symptoms
According to WHO the most common symptoms of Covid-19 are fever, dry cough and tiredness. Other symptoms are aches and pains, nasal congestion, sore throat or diarrhoea. Symptoms usually begin gradually. About 80 % people recover from the disease without needing hospital treatment. Some people have very mild symptoms and there is also number of asymptomatic cases that is yet to be revealed (see table 1).
| Place | Number of positive cases | Proportion of asymptomatic cases | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diamond Princess cruise ship, Yokohama, Japan | 634 | 18% (95% CI 16%-20%) | [1] |
| Shanghai | 328 | 4% | [2] |
| Japanese nationals evacuated from Wuhan | 565 | 31% (95% CI 7.7%-54%) | [3] |
| Long-Term Care Nursing Facility King County, Washington | 23 | 57%* | [4] |
| Hospitalised in Beijing, China | 262 | 5% | [5] |
| Zhejiang Province, China | 391 | 14% | [6] |
| Zhejiang Province, China | 36 (Children) | 28% | [7] |
| People’s Hospital of Daofu county, China | 83 | 22% | [8] |
- Seven days after testing, 10 of 13 asymptomatic patients developed symptoms
Approximately 20 % of patients with Covid-19 become seriously ill and develop difficulty breathing (some of them then have to undertake medical procedures and be put on ventilators or even ECMO).
Chinese scientists described usual development of the diseases in hospitalized patients [9]. They characterized the disease in 138 cases – 26 % required intensive care, the mortality was 4,3 %. The first symptoms were fever, tiredness, muscles aches. The dyspnea came on the fifth day (median; IQR, 1-10) after first symptoms. Patients were hospitalized on the seventh day (median; IQR, 4-8). The acute respiratory distress syndrome came on the eighth day (median; IQR, 6-12). Intensive care was usually needed on the tenth day (median; IQR, 6-12). Patients were released from the hospital on the 17th day.
It is already clear that some people are at higher risk of developing serious illness – mainly older people (65+ years old) and those with underlying medical conditions such as high blood pressure, heart and lung problems, diabetes, or cancer.
Epidemiology
Covid-19 is spread through person to person contact. Primarily through small droplets (containing virus), which are expelled when infected person coughs, sneezes or speaks. Those droplets might spread up to the distance of 2 meters. People can get infected by either inhaling those droplets or by touching objects and surfaces on which those droplets landed earlier and then touching their eyes, nose or mouth. It is not yet known how long does the virus survive outside of human body.
The incubation period ranges from 1 to 14 days, but the average duration between exposure to virus SARS-Cov2 and the onset of the symptoms is usually 5 to 6 days. According to WHO, the basic reproduction number (R0 – the expected number of cases directly generated by one case in a population where all individuals are susceptible to infection) of Covid-19 is 2-3. However the international team of scientists analysed 140 cases across China and determined that a median R0 value is 5.7 (95% CI 3.8–8.9) [10].
As of now we have confirmed 2, 973,264 cases of Covid-19 in the world. The diseases has been confirmed in at least 185 countries / regions and is therefore considered pandemic (announced by WHO on 11th of March 2020). There are 206,569 deaths worldwide so far (written 27th of April 2020). However it is not possible to determine the mortality of Covid-19 yet.
SARS-Cov-2
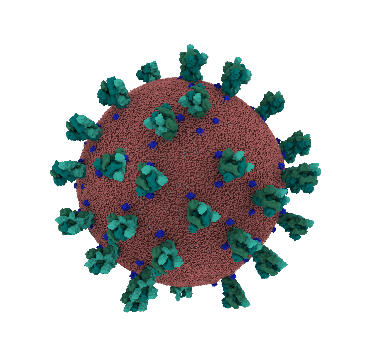
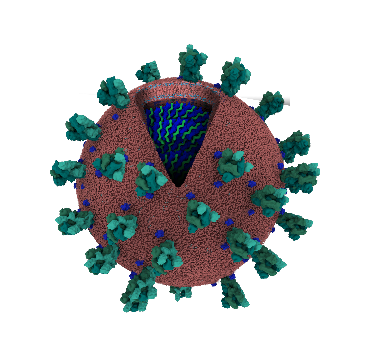
Virus that is causing the disease Covid-19 is a betacoronavirus named SARS-Cov2. It is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus. It´s RNA is less than 30 000 base pairs long (for comparison human genome is over 3 billion base pairs long) and codes 29 proteins. There are 4 structural proteins, 16 non-structural proteins and 9 accessory proteins. Function of some of them is still unknown.
Credit: Maria Voigt/RCSB PDB
One of the most studied proteins is S protein of the coronavirus. S protein is one of the four structural proteins (S, E, M, N) that form the outer layer of the coronavirus and protect the RNA inside. They also help assemble and release new copies of the virus. Spike protein is essential for the virus because it binds to ACE2 receptor on human cells and therefore helps the virus to entry the cell. The gene for the spike protein in SARS-CoV-2 has an insertion of 12 bases: ccucggcgggca. This mutation may help the spikes bind tightly to human cells. After binding the virus entries the cell and hijacks cell´s machinery in order to make own proteins and replicate.
The replication of coronavirus SARS-Cov2 inside the cell
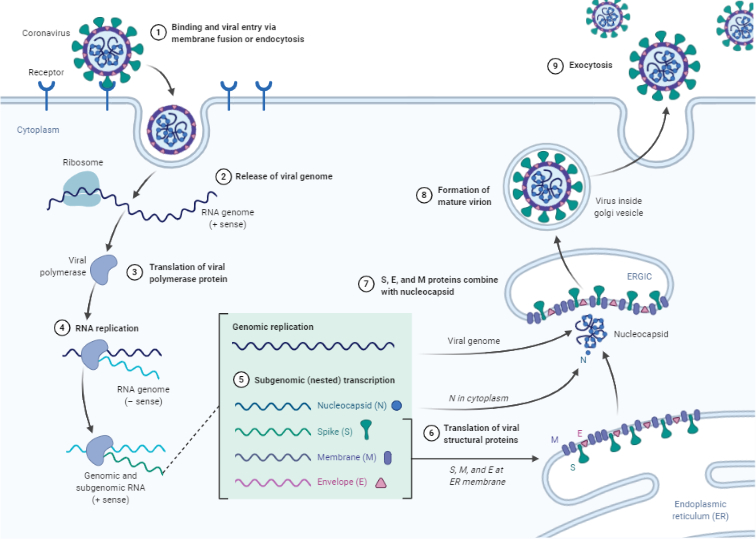
Source: biorender.com
The virus targets mostly lung cells, the virus replicates quickly and the affected alveoli are filling with fluid resulting in the incapability of absorbing oxygen. This leads to the deterioration of capacity of lungs. On top of that the body is undergoing massive immune reaction which can in some events result in cytokine storm – an enormous and uncoordinated immune reaction leading to overall exhaustion and in the worst scenario death.
Possible treatments
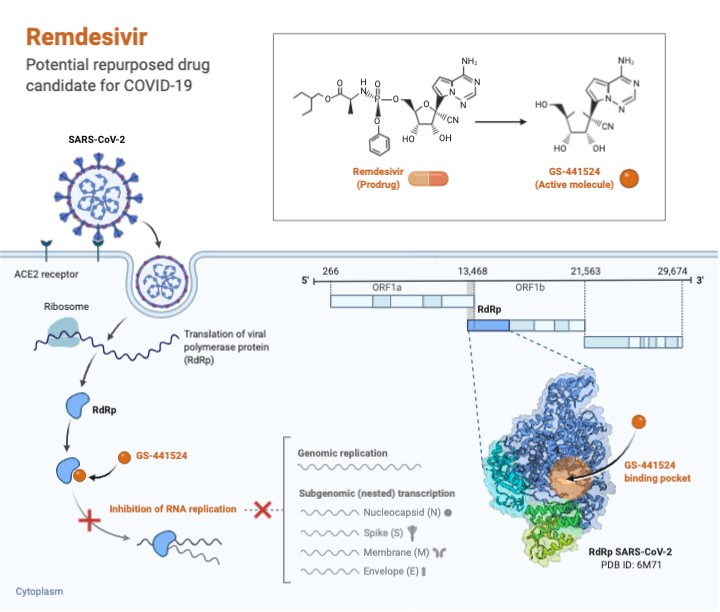
There is no treatment for Covid-19 or vaccine against SARS-Cov2 yet. The most promising candidate seems to be Remdesivir – experimental substance developed by Gilead Sciences. Remdesivir was supposed to beat Ebola virus and it worked, however, scientists found better drugs against Ebola so Remdesivir was set aside. Remdesivir is a prodrug that metabolizes into active molecule that is analogue to adenosine. It then blocks RNA-dependent RNA polymerase – enzyme that is crucial for the replication of virus. Now there are multiple clinical studies trying to prove that Remdesivir is effective against SARS-Cov2.
The effect of Remdesivir on the virus replication
Source: biorender.com
Other promising molecules are Favipiravir or Chloroquine / Hydrochloroquine. Scientists and doctors are also trying to help the patient by suppressing the immune response for example with Tocilizumab. It is a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the binding of interleukin-6 to its receptor.
References
- ↑ Mizumoto K, Kagaya K, Zarebski A, Chowell G. Estimating the asymptomatic proportion of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases on board the Diamond Princess cruise ship, Yokohama, Japan, 2020. Euro Surveill. 2020 Mar;25(10). doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.10.2000180. PMID:32183930 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.10.2000180
- ↑ Zhou X, Li Y, Li T, Zhang W. Follow-up of asymptomatic patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020 Mar 28. pii: S1198-743X(20)30169-5. doi:, 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.03.024. PMID:32234453 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2020.03.024
- ↑ Nishiura H, Kobayashi T, Miyama T, Suzuki A, Jung SM, Hayashi K, Kinoshita R, Yang Y, Yuan B, Akhmetzhanov AR, Linton NM. Estimation of the asymptomatic ratio of novel coronavirus infections (COVID-19). Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 14;94:154-155. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.020. PMID:32179137 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.020
- ↑ Kimball A, Hatfield KM, Arons M, James A, Taylor J, Spicer K, Bardossy AC, Oakley LP, Tanwar S, Chisty Z, Bell JM, Methner M, Harney J, Jacobs JR, Carlson CM, McLaughlin HP, Stone N, Clark S, Brostrom-Smith C, Page LC, Kay M, Lewis J, Russell D, Hiatt B, Gant J, Duchin JS, Clark TA, Honein MA, Reddy SC, Jernigan JA. Asymptomatic and Presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Residents of a Long-Term Care Skilled Nursing Facility - King County, Washington, March 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020 Apr 3;69(13):377-381. doi:, 10.15585/mmwr.mm6913e1. PMID:32240128 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6913e1
- ↑ Tian S, Hu N, Lou J, Chen K, Kang X, Xiang Z, Chen H, Wang D, Liu N, Liu D, Chen G, Zhang Y, Li D, Li J, Lian H, Niu S, Zhang L, Zhang J. Characteristics of COVID-19 infection in Beijing. J Infect. 2020 Apr;80(4):401-406. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.02.018. Epub 2020 Feb , 27. PMID:32112886 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2020.02.018
- ↑ Sun WW, Ling F, Pan JR, Cai J, Miao ZP, Liu SL, Cheng W, Chen EF. [Epidemiological characteristics of 2019 novel coronavirus family clustering in Zhejiang Province]. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Mar 15;54(0):E027. doi:, 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20200227-00199. PMID:32171192 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20200227-00199
- ↑ Qiu H, Wu J, Hong L, Luo Y, Song Q, Chen D. Clinical and epidemiological features of 36 children with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Zhejiang, China: an observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Jun;20(6):689-696. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30198-5. , Epub 2020 Mar 25. PMID:32220650 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30198-5
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.27.20043836
- ↑ Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J, Wang B, Xiang H, Cheng Z, Xiong Y, Zhao Y, Li Y, Wang X, Peng Z. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020 Feb 7. pii: 2761044. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.1585. PMID:32031570 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.1585
- ↑ 10.3201/eid2607.200282