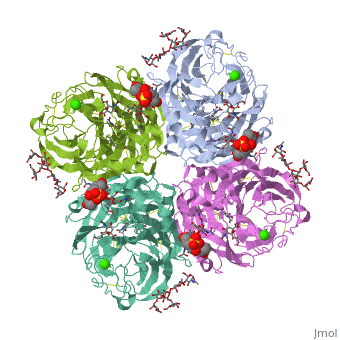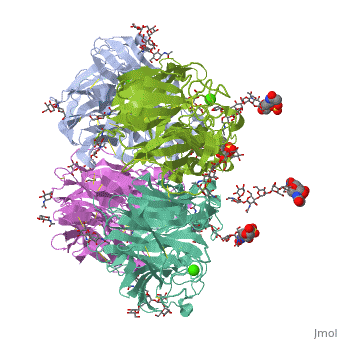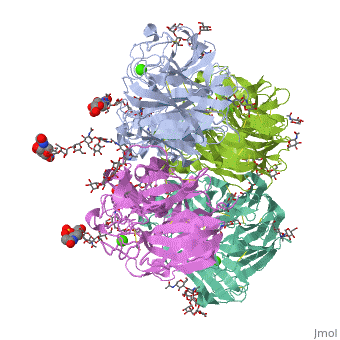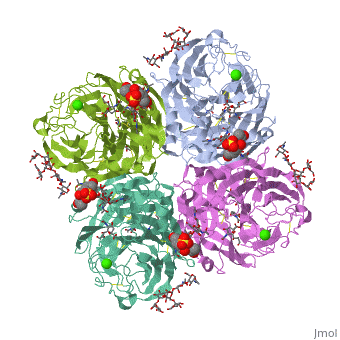2bat
From Proteopedia
THE STRUCTURE OF THE COMPLEX BETWEEN INFLUENZA VIRUS NEURAMINIDASE AND SIALIC ACID, THE VIRAL RECEPTOR
Structural highlights
FunctionNRAM_I67A0 Catalyzes the removal of terminal sialic acid residues from viral and cellular glycoconjugates. Cleaves off the terminal sialic acids on the glycosylated HA during virus budding to facilitate virus release. Additionally helps virus spread through the circulation by further removing sialic acids from the cell surface. These cleavages prevent self-aggregation and ensure the efficient spread of the progeny virus from cell to cell. Otherwise, infection would be limited to one round of replication. Described as a receptor-destroying enzyme because it cleaves a terminal sialic acid from the cellular receptors. May facilitate viral invasion of the upper airways by cleaving the sialic acid moities on the mucin of the airway epithelial cells. Likely to plays a role in the budding process through its association with lipid rafts during intracellular transport. May additionally display a raft-association independent effect on budding. Plays a role in the determination of host range restriction on replication and virulence. Sialidase activity in late endosome/lysosome traffic seems to enhance virus replication. Evolutionary ConservationCheck, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedCrystallographic studies of neuraminidase-sialic acid complexes indicate that sialic acid is distorted on binding the enzyme. Three arginine residues on the enzyme interact with the carboxylate group of the sugar which is observed to be equatorial to the saccharide ring as a consequence of its distorted geometry. The glycosidic oxygen is positioned within hydrogen-bonding distance of Asp-151, implicating this residue in catalysis. The structure of the complex between influenza virus neuraminidase and sialic acid, the viral receptor.,Varghese JN, McKimm-Breschkin JL, Caldwell JB, Kortt AA, Colman PM Proteins. 1992 Nov;14(3):327-32. PMID:1438172[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
| ||||||||||||||||||||