α-actinin-2
Introduction
Muscle cells are responsible for the voluntary and involuntary contraction. These cells contains myofibrils, which are bundles mainly formed by actin and myosin filaments. These filaments are organized into repetitive subunits, called sarcomeres, which are connected in tandem by Z-disks, constituting an intricate macromolecular assembly. A plethora of proteins have been identified in the Z-disk [[1]], members of different protein classes - globular, intrinsically disordered and multi-domain proteins, but the details about their structure and interaction network at molecular level are still an enigma. Understanding how these proteins work together and how they interact with other molecules can have major impacts in medicine.
The protein α-actinin skeletal muscle isoform 2 (α-actinin-2) has a pivotal role in the formation and integrity of the ultra-structure of striated muscle Z-disk[1]. Including, in the beginning steps of progression of the Z-bodies in premyofibrils and nascent myofibrils to Z-disks of the mature myofibrils [2].
α-actinin-2 is a calcium-independent isoform expressed in all muscle fibers. The expression in human skeletal muscle overlaps α-actinin-3. Both proteins form heterodimers in vitro and in vivo and share high protein sequence identity (80%), therefore suggesting a high 3-D structure similarity. They are regulated by phosphoinositides, rendering alpha-actinin capable of binding to titin (and some other Z-disk partners). It is worth pointing out that the other α-actinin non-muscles isoforms (1 and 4) are calcium-dependent. α-actinin-1 is associate with cell adhesion molecules, stabilizing cell adhesion and regulating cell shape and cell motility, while α-actinin-4 are related to the cytoskeleton playing an essential role in cell motility and shape and tumor suppressor activity.
Sequence annotation and interaction network
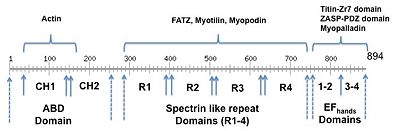
α-actinin-2 (UNIPROT) protein is composed of 894 residues organized in a modular fashion (Scheme 1). At the N-terminus it is identified two calponin homology domains (CH), also called actin biding domain(ABD), followed by four spectrin-like repeats domains (R1-4 domain) - referred as rod domain. Finally, the C-terminus is composed of a CaM-like domain (EFhands 1-4). The quaternary structure of α-actinin-2 is constituted of a stable antiparellel homodimer (~200 kDa) that cross-links anti-parallel actin filaments and interacts with titin[[2]] mediated by ABD domain and EF-hand domain, respectively.
Scheme 1 - α-actinin-2 domains according to the protein residues (bottom panel). On the top panel, some α-actinin-2 protein binding partners are indicated.
At the ABD domain three actin binding sites (ABS) are mapped to be important for the interaction to F-actin. ABS 1 and 2 spanning the amino acids residues 48–57 and 123–147, which are located at the CH1 domain, while ABS 2 (residues 153–172) are found at the CH2 domain [3]. The spectrin like repeats of α-actinin-2 are required for the binding to the C-terminal region of the FATZ [3], and myotilin [4], myopodin [5]. EF3-4 domains of α-actinin-2 binds Z-repeat 1 and 7 of titin simultaneously to PDZ domain of ZASP protein [6] [4] [5]. For the complete list of α-actinin-2 Z-disc protein partners access the following link [[7]]
The skeletal isoform 2 and 3 are Ca+2-independent isoform protein that seems to be regulate by phosphatidylinositol 4, 5 biphosphate (PIP2). The molecular details of this interaction are not well understood. But, there are evidences that PIP2 interact on the ABD domains [6] in one hand increasing F-actin:α-actinin cross-linking activity [7] and in other hand inducing conformation changes in α-actinin-2 that in turn leads the binding of EF3-4 domains to titin [8].
Structures
Current structural data of the isoform 2 suggest an autoinhibited closed conformation where the C-terminal lobe of the calmodulin-like domain is bound to the α-helix that connects the ABD domain to the first spectrin-like repeat. A gallery of additional structures of α-actinin fragments are also available (see the link)[[8]]. The ABD domain reveals the arrangement of the two calponin homology domains (CH1 and CH2) in a closed conformation[3]
The rod domain shows the four spectrins like domain of one chain forms a homo anti-parallel dimer, which is a left handed twisted from one end of the rod to the other end [9].
The solution structure of the complex between the human α-actinin-2 EF-hand domain and the chicken titin Z-repeat 7 domain was solved by NMR spectroscopy. A specific set of contacts and some important residues for protein-protein interactions were identified. It was shown that recognition and positioning of Z-repeat in cavity of EF-hand domain is mediated by balance of electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions. The reported semi-open conformation of complex is commonly seen in homologous structures. This conformation seems to be typical for calcium-independent recognition by EF-hand domain and is fully compatible with formation of stable long-term complexes between titin and α-actinin-2.
Pathology
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a genetically transmitted disease and an important cause of morbidity and sudden cardiac death in young people, including competitive athletes [10]. Recently, Chiu et al (2010) [11] have reported a list of point mutation in the ACTN2 gene related to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (Gln9Arg, Gly111Val, Ala119Thr, Thr495Met, Glu583Ala, Glu628Gly, Arg759Thr). However, the impact of these mutation in the α-actinin-2 protein structure and function is poorly understood.