Reserved Sandbox 329
From Proteopedia
Contents |
Uridylyl transferases
INTRODUCTION
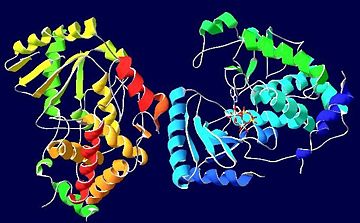
Terminal uridylyl transferases (TUTases) belong to a superfamily of polymerase ß nucleotidyl transferases.[1] TUTases have been isolated from Trypanosoma brucei and also Leishmania ssp, parasites causing diseases in humans such as African Sleeping Sickness.[2] TUTases function in RNA editing; more specifically they catalyze the reaction that adds UMP to a RNA substrate. Trypanosomal TUTases have RNA substrates that are shown to select for cognate nucleosides and provide a metal ion binding site for Mg2+ ions.[1]
| |||||||||
| 2q0d, resolution 2.00Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , | ||||||||
| Gene: | TUT4 (Trypanosoma brucei) | ||||||||
| Activity: | RNA uridylyltransferase, with EC number 2.7.7.52 | ||||||||
| Related: | 2ikf, 2nom | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
STRUCTURE
The uridylyl transferase bound ligand is an with two Mg2+ ions, however many TUTases involved in RNA editing are shown to exhibit preference for binding to UTP instead.[1] Three are conserved in TUTases, and are required for coordinating the Mg2+ ions in some TUTases. [1] Thus, these are vital in catalyzing this reaction.
REFERENCES
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Stagno J, Aphasizheva I, Aphasizhev R, Luecke H. Dual role of the RNA substrate in selectivity and catalysis by terminal uridylyl transferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Sep 11;104(37):14634-9. Epub 2007 Sep 4. PMID:17785418
- ↑ Aphasizhev R, Sbicego S, Peris M, Jang SH, Aphasizheva I, Simpson AM, Rivlin A, Simpson L. Trypanosome mitochondrial 3' terminal uridylyl transferase (TUTase): the key enzyme in U-insertion/deletion RNA editing. Cell. 2002 Mar 8;108(5):637-48. PMID:11893335