User:Udayan Shevade/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
Contents |
SV40 Large T Antigen
Introduction
The SV40 large tumor antigen is a multifunctional regulatory protein encoded by Simian Virus 40. It is classified under the AAA+ family of helicases [1]. The protein is responsible for initiation of viral DNA replication, regulation of viral transcription and transformation of the host cell to promote viral infectivity. Large T-antigen is an early gene product of SV40 and is produced via differential mRNA splicing.
Structure and Function
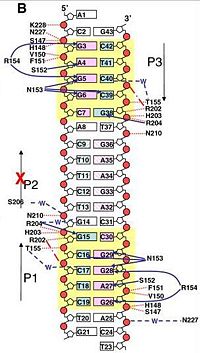
T antigen is a 708-amino acid protein consisting of three major domains: an N-terminal J domain, a central origin-binding domain, and a C-terminal helicase domain [2].
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||
| 1svm, resolution 1.94Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , | ||||||||
| Related: | 1svl, 1svo | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
Helicase
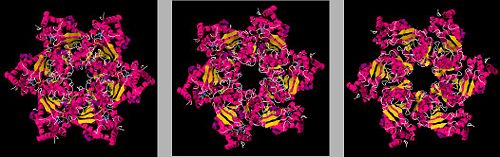
The consists of a AAA+ domain. Each monomer binds and hydrolyzes an ATP at this region in the presence of magnesium ion. Together, the monomers drive an overall conformational change in the hexamer. The helicase monomer can exist in one of three states: ATP-bound, ADP-bound and Nt-free. The transitions in conformation between these states enable the unwinding of viral dsDNA. There are both cis- and trans-monomer interactions involving ATP.
Lys432, Thr433 and Thr434 of the P loop interact closely with the triphosphate groups, and Asp474 and Asn529 form H bonds with ATP on the same residue. Among these, Ilu428, Thr433 and Asp474 adopt different conformations in the ADP-bound state. In the Nt-free state, Ilu428 and Thr434 are turned even further and sterically disallow the presence of ADP.
near the ATP is present for stability and nucleophilic attack during hydrolysis.
, of which Lys418 and Lys419 stabilize ATP hydrolysis, interact with ATP on adjacent monomers, important in producing conformational changes.
These rearrangements affect the position of a positively-charged structure that protrudes into the central channel. Trans-residues Arg498, Asp499 and Asp502 are located at the base of the hairpin, lending a lever-like functionality. The motion of the β hairpin unwinds the DNA through the central channel [5].
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Luo X, Sanford DG, Bullock PA, Bachovchin WW. Solution structure of the origin DNA-binding domain of SV40 T-antigen. Nat Struct Biol. 1996 Dec;3(12):1034-9. PMID:8946857
- ↑ Gai D, Zhao R, Li D, Finkielstein CV, Chen XS. Mechanisms of conformational change for a replicative hexameric helicase of SV40 large tumor antigen. Cell. 2004 Oct 1;119(1):47-60. PMID:15454080 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.017
- ↑ Falchuk KH, Czupryn M. Isolation of metallothioneins under metal-free conditions. Methods Enzymol. 1991;205:47-53. PMID:1779811
- ↑ Shafer WM, Onunka VC. Mechanism of staphylococcal resistance to non-oxidative antimicrobial action of neutrophils: importance of pH and ionic strength in determining the bactericidal action of cathepsin G. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Apr;135(4):825-30. PMID:2600586
- ↑ Gai D, Zhao R, Li D, Finkielstein CV, Chen XS. Mechanisms of conformational change for a replicative hexameric helicase of SV40 large tumor antigen. Cell. 2004 Oct 1;119(1):47-60. PMID:15454080 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.017
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Jezequel J, Cambeau M, Becuwe B, Daniel C. [Fractures of the face. Craniofacial dislocations and comminution of the middle protion of the face]. J Fr Otorhinolaryngol Audiophonol Chir Maxillofac. 1977 Mar;26(3):203-18. PMID:140208
- ↑ Kelley WL, Georgopoulos C. Positive control of the two-component RcsC/B signal transduction network by DjlA: a member of the DnaJ family of molecular chaperones in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1997 Sep;25(5):913-31. PMID:9364917
- ↑ Mitrofanov PM. [Pathomorphology in chlamydial-parainfluenzal infection in calves]. Veterinariia. 1979 Jul;(7):35-8. PMID:232328
- ↑ Lee JO, Russo AA, Pavletich NP. Structure of the retinoblastoma tumour-suppressor pocket domain bound to a peptide from HPV E7. Nature. 1998 Feb 26;391(6670):859-65. PMID:9495340 doi:10.1038/36038