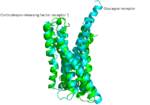
We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1181
From Proteopedia
|
Old Stuff:
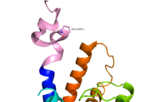
Fig. 1: A135P Mutation and effect on stalk stability [1].
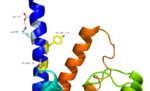
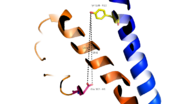
Fig. 2: Stalk stabilized by salt bridge between Glu133-Lys136. Residues in yellow are demonstrated to have an effect on ligand binding affinity.[1]
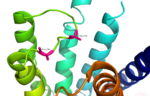
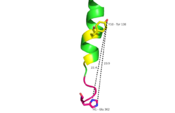
Fig. 3: Active sites linked to glucagon binding affinity located on ECL1 are labeled[1].
Future research direction
Research for Class A GPCRs is much more extensive than for its secretin, class B counterparts, although class B is proving to be a worthwhile to invest researching. The challenge of class B stabilization, expression, and molecular size , has made class B GPCRs particularly hard to assay. Biochemical research has increased in the class B specifications, because it has been realized that receptors can be modulated by more than the agonist and antagonists present in vivo. Leading research consists of a complex interwoven scheme of equilibria manipulation in multi-receptor conformations. [2]