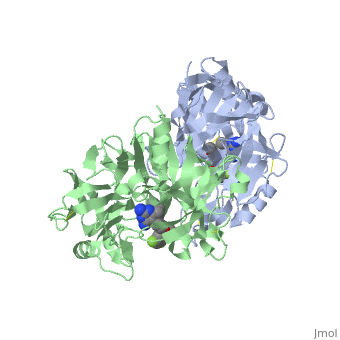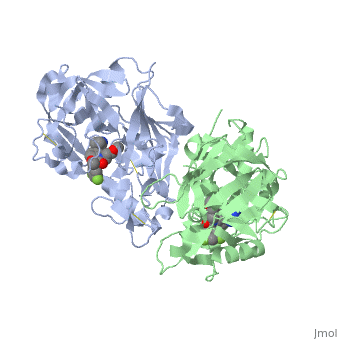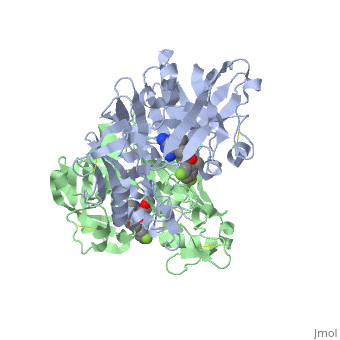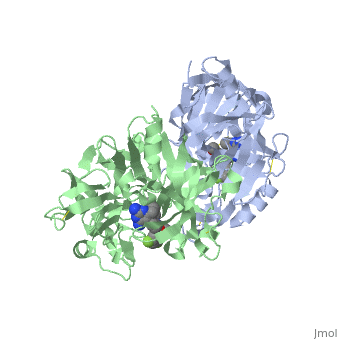We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
CHEM2052 Tutorial Example4
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Background == | == Background == | ||
| - | In later lecture we will look a little more closely at '''Renin''' (also known as '''angiotensinase'''). This enzyme is involved in a biological pathway leading to elevation of blood pressure, which can be beneficial in many ways. However if this process has become overactive, hypertension (high blood pressure) can result. Hypertension leads to cardiovascular disease which is the leading cause of death globally. The World Health Organisation states "An estimated 17.3 million people died from cardiovascular disease in 2008, representing 30% of all global deaths" see the following web page if you want to know more: [http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/en/]. | + | In later lecture we will look a little more closely at '''Renin''' (also known as '''angiotensinase'''). This enzyme is involved in a biological pathway leading to elevation of blood pressure, which can be beneficial in many ways. However if this process has become overactive, hypertension (high blood pressure) can result. Hypertension leads to cardiovascular disease which is the leading cause of death globally. The World Health Organisation states "An estimated 17.3 million people died from cardiovascular disease in 2008, representing 30% of all global deaths" see the following web page if you want to know more: [http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/en/ Cardiovascular disease facts WHO]. |
Since the 1970s scientists have been trying to modulate the action of renin by blocking the active site of the enzyme and preventing its function, hence lowering blood pressure. Aliskerin is the only renin inhibitor in clinical use today [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Renin_inhibitor Renin information Site]. However there is still interest in developing new, improved inhibitors. This question looks at a renin inhibitor identified through research at Pfizer.<ref>PMID:17574423</ref> | Since the 1970s scientists have been trying to modulate the action of renin by blocking the active site of the enzyme and preventing its function, hence lowering blood pressure. Aliskerin is the only renin inhibitor in clinical use today [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Renin_inhibitor Renin information Site]. However there is still interest in developing new, improved inhibitors. This question looks at a renin inhibitor identified through research at Pfizer.<ref>PMID:17574423</ref> | ||
Revision as of 04:41, 13 August 2014
CHEM2052_Tutorial_Example4
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Powell NA, Ciske FL, Cai C, Holsworth DD, Mennen K, Van Huis CA, Jalaie M, Day J, Mastronardi M, McConnell P, Mochalkin I, Zhang E, Ryan MJ, Bryant J, Collard W, Ferreira S, Gu C, Collins R, Edmunds JJ. Rational design of 6-(2,4-diaminopyrimidinyl)-1,4-benzoxazin-3-ones as small molecule renin inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007 Sep 1;15(17):5912-49. Epub 2007 Jun 2. PMID:17574423 doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2007.05.069
- ↑ Rawlings ND, Morton FR, Kok CY, Kong J, Barrett AJ. MEROPS: the peptidase database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D320-5. Epub 2007 Nov 8. PMID:17991683 doi:10.1093/nar/gkm954
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Di Cera E. Serine proteases. IUBMB Life. 2009 May;61(5):510-5. PMID:19180666 doi:10.1002/iub.186