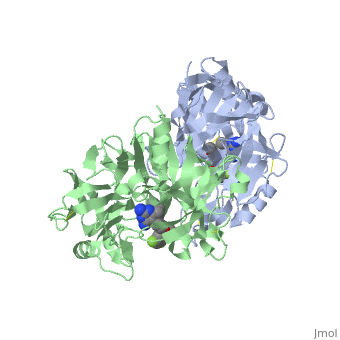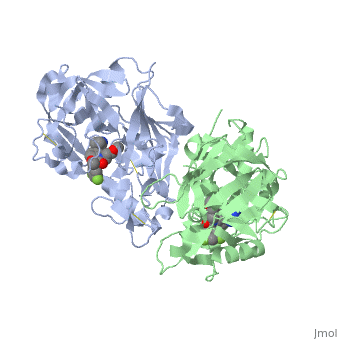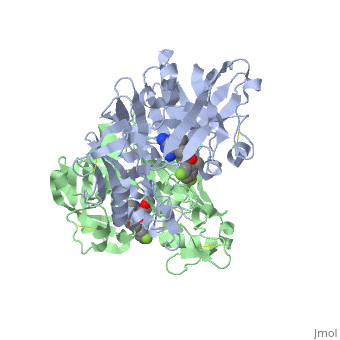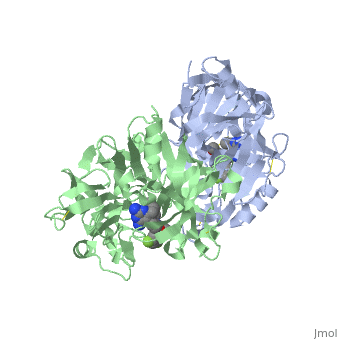We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
CHEM2052 Tutorial Example4
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
== '''Active Site Interactions''' == | == '''Active Site Interactions''' == | ||
| - | + | This inhibitor does not just bind to the catalytic residues there are many other amino acids at the active site of the enzyme. First predict possible interaction types you would expect with this structure. Then look at the 2-dimensional "map" of the active site provided on your tutorial sheet and compare this to the 3-dimensional representations here. | |
| - | This view shows the amino acid residues on the left hand side of your "map". | + | This view shows the amino acid residues on the left hand side of your "map". You may notice that these amino acids are fairly hydrophobic and interact with the hydrophobic parts of the inhibitor. |
| - | + | Similarly this view shows the amino acid residues on the right hand side of your "map". | |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 08:15, 13 August 2014
CHEM2052_Tutorial_Example4
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Powell NA, Ciske FL, Cai C, Holsworth DD, Mennen K, Van Huis CA, Jalaie M, Day J, Mastronardi M, McConnell P, Mochalkin I, Zhang E, Ryan MJ, Bryant J, Collard W, Ferreira S, Gu C, Collins R, Edmunds JJ. Rational design of 6-(2,4-diaminopyrimidinyl)-1,4-benzoxazin-3-ones as small molecule renin inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007 Sep 1;15(17):5912-49. Epub 2007 Jun 2. PMID:17574423 doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2007.05.069