| Structural highlights
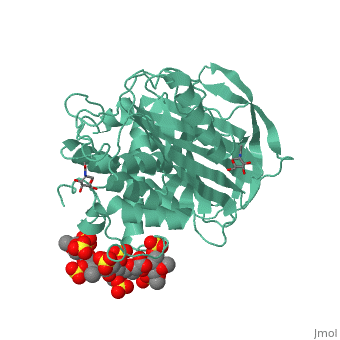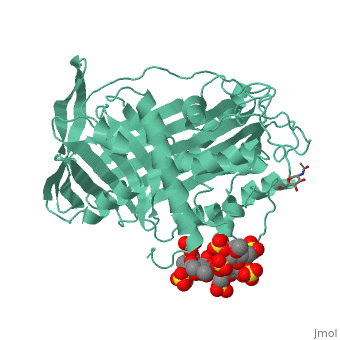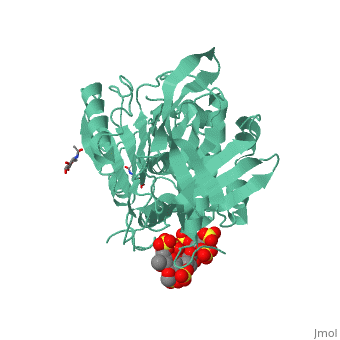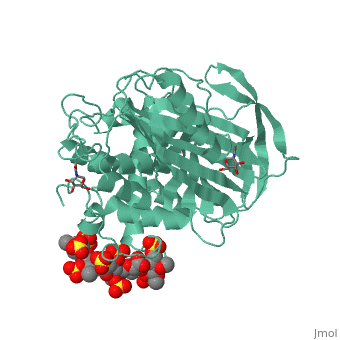
1azx is a 2 chain structure with sequence from Homo sapiens. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA. For a guided tour on the structure components use FirstGlance.
| | Method: | X-ray diffraction, Resolution 2.9Å |
| Ligands: | , , , , , , |
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBe, RCSB, PDBsum, ProSAT |
Disease
ANT3_HUMAN Defects in SERPINC1 are the cause of antithrombin III deficiency (AT3D) [MIM:613118. AT3D is an important risk factor for hereditary thrombophilia, a hemostatic disorder characterized by a tendency to recurrent thrombosis. AT3D is classified into 4 types. Type I: characterized by a 50% decrease in antigenic and functional levels. Type II: has defects affecting the thrombin-binding domain. Type III: alteration of the heparin-binding domain. Plasma AT-III antigen levels are normal in type II and III. Type IV: consists of miscellaneous group of unclassifiable mutations.[1] [:][2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [:][23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] [31] [32] [33] [34] [35]
Function
ANT3_HUMAN Most important serine protease inhibitor in plasma that regulates the blood coagulation cascade. AT-III inhibits thrombin, matriptase-3/TMPRSS7, as well as factors IXa, Xa and XIa. Its inhibitory activity is greatly enhanced in the presence of heparin.[36]
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
Antithrombin, a plasma serpin, is relatively inactive as an inhibitor of the coagulation proteases until it binds to the heparan side chains that line the microvasculature. The binding specifically occurs to a core pentasaccharide present both in the heparans and in their therapeutic derivative heparin. The accompanying conformational change of antithrombin is revealed in a 2.9-A structure of a dimer of latent and active antithrombins, each in complex with the high-affinity pentasaccharide. Inhibitory activation results from a shift in the main sheet of the molecule from a partially six-stranded to a five-stranded form, with extrusion of the reactive center loop to give a more exposed orientation. There is a tilting and elongation of helix D with the formation of a 2-turn helix P between the C and D helices. Concomitant conformational changes at the heparin binding site explain both the initial tight binding of antithrombin to the heparans and the subsequent release of the antithrombin-protease complex into the circulation. The pentasaccharide binds by hydrogen bonding of its sulfates and carboxylates to Arg-129 and Lys-125 in the D-helix, to Arg-46 and Arg-47 in the A-helix, to Lys-114 and Glu-113 in the P-helix, and to Lys-11 and Arg-13 in a cleft formed by the amino terminus. This clear definition of the binding site will provide a structural basis for developing heparin analogues that are more specific toward their intended target antithrombin and therefore less likely to exhibit side effects.
The anticoagulant activation of antithrombin by heparin.,Jin L, Abrahams JP, Skinner R, Petitou M, Pike RN, Carrell RW Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Dec 23;94(26):14683-8. PMID:9405673[37]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Lindo VS, Kakkar VV, Learmonth M, Melissari E, Zappacosta F, Panico M, Morris HR. Antithrombin-TRI (Ala382 to Thr) causing severe thromboembolic tendency undergoes the S-to-R transition and is associated with a plasma-inactive high-molecular-weight complex of aggregated antithrombin. Br J Haematol. 1995 Mar;89(3):589-601. PMID:7734359
- ↑ Bock SC, Marrinan JA, Radziejewska E. Antithrombin III Utah: proline-407 to leucine mutation in a highly conserved region near the inhibitor reactive site. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):6171-8. PMID:3191114
- ↑ Lane DA, Bayston T, Olds RJ, Fitches AC, Cooper DN, Millar DS, Jochmans K, Perry DJ, Okajima K, Thein SL, Emmerich J. Antithrombin mutation database: 2nd (1997) update. For the Plasma Coagulation Inhibitors Subcommittee of the Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Thromb Haemost. 1997 Jan;77(1):197-211. PMID:9031473
- ↑ Koide T, Odani S, Takahashi K, Ono T, Sakuragawa N. Antithrombin III Toyama: replacement of arginine-47 by cysteine in hereditary abnormal antithrombin III that lacks heparin-binding ability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):289-93. PMID:6582486
- ↑ Chang JY, Tran TH. Antithrombin III Basel. Identification of a Pro-Leu substitution in a hereditary abnormal antithrombin with impaired heparin cofactor activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1174-6. PMID:3080419
- ↑ Stephens AW, Thalley BS, Hirs CH. Antithrombin-III Denver, a reactive site variant. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1044-8. PMID:3805013
- ↑ Devraj-Kizuk R, Chui DH, Prochownik EV, Carter CJ, Ofosu FA, Blajchman MA. Antithrombin-III-Hamilton: a gene with a point mutation (guanine to adenine) in codon 382 causing impaired serine protease reactivity. Blood. 1988 Nov;72(5):1518-23. PMID:3179438
- ↑ Erdjument H, Lane DA, Panico M, Di Marzo V, Morris HR. Single amino acid substitutions in the reactive site of antithrombin leading to thrombosis. Congenital substitution of arginine 393 to cysteine in antithrombin Northwick Park and to histidine in antithrombin Glasgow. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5589-93. PMID:3162733
- ↑ Erdjument H, Lane DA, Panico M, Di Marzo V, Morris HR, Bauer K, Rosenberg RD. Antithrombin Chicago, amino acid substitution of arginine 393 to histidine. Thromb Res. 1989 Jun 15;54(6):613-9. PMID:2781509
- ↑ Borg JY, Brennan SO, Carrell RW, George P, Perry DJ, Shaw J. Antithrombin Rouen-IV 24 Arg----Cys. The amino-terminal contribution to heparin binding. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 18;266(1-2):163-6. PMID:2365065
- ↑ Gandrille S, Aiach M, Lane DA, Vidaud D, Molho-Sabatier P, Caso R, de Moerloose P, Fiessinger JN, Clauser E. Important role of arginine 129 in heparin-binding site of antithrombin III. Identification of a novel mutation arginine 129 to glutamine. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18997-9001. PMID:2229057
- ↑ Austin RC, Rachubinski RA, Blajchman MA. Site-directed mutagenesis of alanine-382 of human antithrombin III. FEBS Lett. 1991 Mar 25;280(2):254-8. PMID:2013320
- ↑ Perry DJ, Daly M, Harper PL, Tait RC, Price J, Walker ID, Carrell RW. Antithrombin Cambridge II, 384 Ala to Ser. Further evidence of the role of the reactive centre loop in the inhibitory function of the serpins. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 22;285(2):248-50. PMID:1906811
- ↑ Olds RJ, Lane DA, Boisclair M, Sas G, Bock SC, Thein SL. Antithrombin Budapest 3. An antithrombin variant with reduced heparin affinity resulting from the substitution L99F. FEBS Lett. 1992 Apr 6;300(3):241-6. PMID:1555650
- ↑ Blajchman MA, Fernandez-Rachubinski F, Sheffield WP, Austin RC, Schulman S. Antithrombin-III-Stockholm: a codon 392 (Gly----Asp) mutation with normal heparin binding and impaired serine protease reactivity. Blood. 1992 Mar 15;79(6):1428-34. PMID:1547341
- ↑ Okajima K, Abe H, Maeda S, Motomura M, Tsujihata M, Nagataki S, Okabe H, Takatsuki K. Antithrombin III Nagasaki (Ser116-Pro): a heterozygous variant with defective heparin binding associated with thrombosis. Blood. 1993 Mar 1;81(5):1300-5. PMID:8443391
- ↑ Olds RJ, Lane DA, Beresford CH, Abildgaard U, Hughes PM, Thein SL. A recurrent deletion in the antithrombin gene, AT106-108(-6 bp), identified by DNA heteroduplex detection. Genomics. 1993 Apr;16(1):298-9. PMID:8486379 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/geno.1993.1184
- ↑ Emmerich J, Vidaud D, Alhenc-Gelas M, Chadeuf G, Gouault-Heilmann M, Aillaud MF, Aiach M. Three novel mutations of antithrombin inducing high-molecular-mass compounds. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994 Dec;14(12):1958-65. PMID:7981186
- ↑ Millar DS, Wacey AI, Ribando J, Melissari E, Laursen B, Woods P, Kakkar VV, Cooper DN. Three novel missense mutations in the antithrombin III (AT3) gene causing recurrent venous thrombosis. Hum Genet. 1994 Nov;94(5):509-12. PMID:7959685
- ↑ Jochmans K, Lissens W, Vervoort R, Peeters S, De Waele M, Liebaers I. Antithrombin-Gly 424 Arg: a novel point mutation responsible for type 1 antithrombin deficiency and neonatal thrombosis. Blood. 1994 Jan 1;83(1):146-51. PMID:8274732
- ↑ van Boven HH, Olds RJ, Thein SL, Reitsma PH, Lane DA, Briet E, Vandenbroucke JP, Rosendaal FR. Hereditary antithrombin deficiency: heterogeneity of the molecular basis and mortality in Dutch families. Blood. 1994 Dec 15;84(12):4209-13. PMID:7994035
- ↑ Bruce D, Perry DJ, Borg JY, Carrell RW, Wardell MR. Thromboembolic disease due to thermolabile conformational changes of antithrombin Rouen-VI (187 Asn-->Asp) J Clin Invest. 1994 Dec;94(6):2265-74. PMID:7989582 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI117589
- ↑ Emmerich J, Chadeuf G, Alhenc-Gelas M, Gouault-Heilman M, Toulon P, Fiessinger JN, Aiach M. Molecular basis of antithrombin type I deficiency: the first large in-frame deletion and two novel mutations in exon 6. Thromb Haemost. 1994 Oct;72(4):534-9. PMID:7878627
- ↑ Okajima K, Abe H, Wagatsuma M, Okabe H, Takatsuki K. Antithrombin III Kumamoto II; a single mutation at Arg393-His increased the affinity of antithrombin III for heparin. Am J Hematol. 1995 Jan;48(1):12-8. PMID:7832187
- ↑ Ozawa T, Takikawa Y, Niiya K, Fujiwara T, Suzuki K, Sato S, Sakuragawa N. Antithrombin Morioka (Cys 95-Arg): a novel missense mutation causing type I antithrombin deficiency. Thromb Haemost. 1997 Feb;77(2):403. PMID:9157604
- ↑ Fitches AC, Appleby R, Lane DA, De Stefano V, Leone G, Olds RJ. Impaired cotranslational processing as a mechanism for type I antithrombin deficiency. Blood. 1998 Dec 15;92(12):4671-6. PMID:9845533
- ↑ Jochmans K, Lissens W, Seneca S, Capel P, Chatelain B, Meeus P, Osselaer JC, Peerlinck K, Seghers J, Slacmeulder M, Stibbe J, van de Loo J, Vermylen J, Liebaers I, De Waele M. The molecular basis of antithrombin deficiency in Belgian and Dutch families. Thromb Haemost. 1998 Sep;80(3):376-81. PMID:9759613
- ↑ Picard V, Bura A, Emmerich J, Alhenc-Gelas M, Biron C, Houbouyan-Reveillard LL, Molho P, Labatide-Alanore A, Sie P, Toulon P, Verdy E, Aiach M. Molecular bases of antithrombin deficiency in French families: identification of seven novel mutations in the antithrombin gene. Br J Haematol. 2000 Sep;110(3):731-4. PMID:10997988
- ↑ Niiya K, Kiguchi T, Dansako H, Fujimura K, Fujimoto T, Iijima K, Tanimoto M, Harada M. Two novel gene mutations in type I antithrombin deficiency. Int J Hematol. 2001 Dec;74(4):469-72. PMID:11794707
- ↑ Baud O, Picard V, Durand P, Duchemin J, Proulle V, Alhenc-Gelas M, Devictor D, Dreyfus M. Intracerebral hemorrhage associated with a novel antithrombin gene mutation in a neonate. J Pediatr. 2001 Nov;139(5):741-3. PMID:11713457 doi:10.1067/mpd.2001.118191
- ↑ Mushunje A, Zhou A, Huntington JA, Conard J, Carrell RW. Antithrombin 'DREUX' (Lys 114Glu): a variant with complete loss of heparin affinity. Thromb Haemost. 2002 Sep;88(3):436-43. PMID:12353073 doi:10.1267/THRO88030436
- ↑ Picard V, Dautzenberg MD, Villoutreix BO, Orliaguet G, Alhenc-Gelas M, Aiach M. Antithrombin Phe229Leu: a new homozygous variant leading to spontaneous antithrombin polymerization in vivo associated with severe childhood thrombosis. Blood. 2003 Aug 1;102(3):919-25. Epub 2003 Feb 20. PMID:12595305 doi:10.1182/blood-2002-11-3391
- ↑ Nagaizumi K, Inaba H, Amano K, Suzuki M, Arai M, Fukutake K. Five novel and four recurrent point mutations in the antithrombin gene causing venous thrombosis. Int J Hematol. 2003 Jul;78(1):79-83. PMID:12894857
- ↑ David D, Ribeiro S, Ferrao L, Gago T, Crespo F. Molecular basis of inherited antithrombin deficiency in Portuguese families: identification of genetic alterations and screening for additional thrombotic risk factors. Am J Hematol. 2004 Jun;76(2):163-71. PMID:15164384 doi:10.1002/ajh.20067
- ↑ Kuhli C, Jochmans K, Scharrer I, Luchtenberg M, Hattenbach LO. Retinal vein occlusion associated with antithrombin deficiency secondary to a novel G9840C missense mutation. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006 Aug;124(8):1165-9. PMID:16908819 doi:10.1001/archopht.124.8.1165
- ↑ Szabo R, Netzel-Arnett S, Hobson JP, Antalis TM, Bugge TH. Matriptase-3 is a novel phylogenetically preserved membrane-anchored serine protease with broad serpin reactivity. Biochem J. 2005 Aug 15;390(Pt 1):231-42. PMID:15853774 doi:BJ20050299
- ↑ Jin L, Abrahams JP, Skinner R, Petitou M, Pike RN, Carrell RW. The anticoagulant activation of antithrombin by heparin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Dec 23;94(26):14683-8. PMID:9405673
|