Structural highlights
Function
Q25735_PLAFA
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
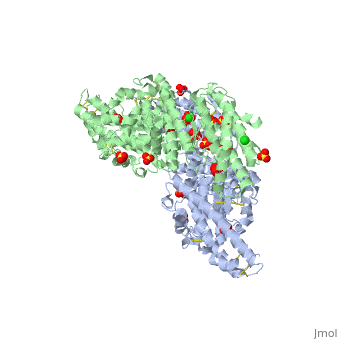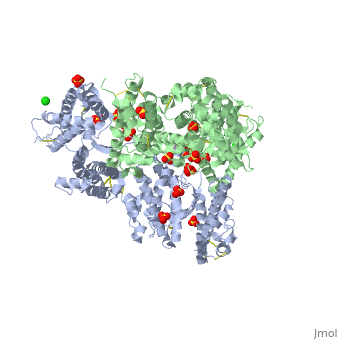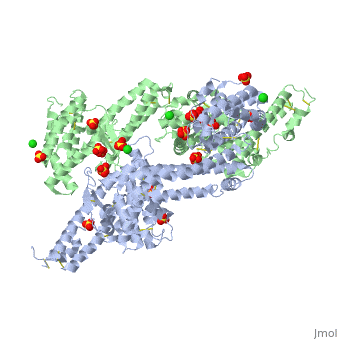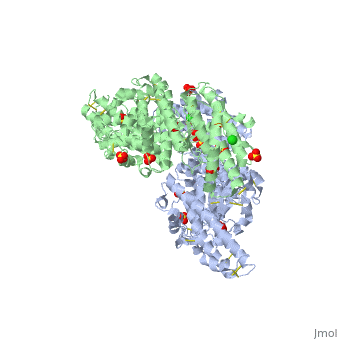
Erythrocyte binding antigen 175 (EBA-175) is a P. falciparum protein that binds the major glycoprotein found on human erythrocytes, glycophorin A, during invasion. Here we present the crystal structure of the erythrocyte binding domain of EBA-175, RII, which has been established as a vaccine candidate. Binding sites for the heavily sialylated receptor glycophorin A are proposed based on a complex of RII with a glycan that contains the essential components required for binding. The dimeric organization of RII displays two prominent channels that contain four of the six observed glycan binding sites. Each monomer consists of two Duffy binding-like (DBL) domains (F1 and F2). F2 more prominently lines the channels and makes the majority of the glycan contacts, underscoring its role in cytoadherence and in antigenic variation in malaria. Our studies provide insight into the mechanism of erythrocyte invasion by the malaria parasite and aid in rational drug design and vaccines.
Structural basis for the EBA-175 erythrocyte invasion pathway of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum.,Tolia NH, Enemark EJ, Sim BK, Joshua-Tor L Cell. 2005 Jul 29;122(2):183-93. PMID:16051144[1]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Tolia NH, Enemark EJ, Sim BK, Joshua-Tor L. Structural basis for the EBA-175 erythrocyte invasion pathway of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Cell. 2005 Jul 29;122(2):183-93. PMID:16051144 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.05.033