Structural highlights
Function
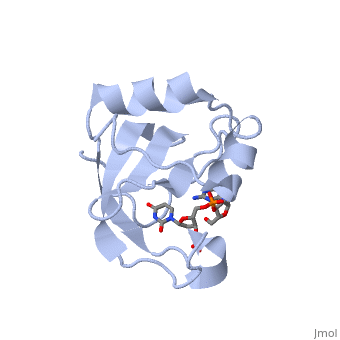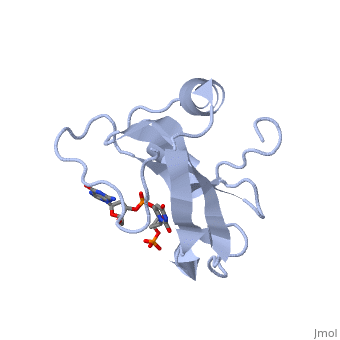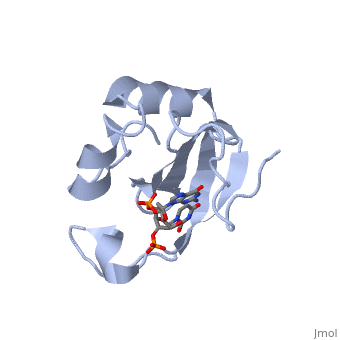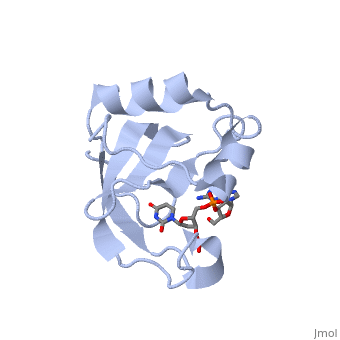
CEA5_ECOLX Colicins are polypeptide toxins produced by and active against E.coli and closely related bacteria. This colicin is an endonuclease.
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
Colicin E5--a tRNase toxin--specifically cleaves QUN (Q: queuosine) anticodons of the Escherichia coli tRNAs for Tyr, His, Asn and Asp. Here, we report the crystal structure of the C-terminal ribonuclease domain (CRD) of E5 complexed with a substrate analog, namely, dGpdUp, at a resolution of 1.9 A. Thisstructure is the first to reveal the substrate recognition mechanism of sequence-specific ribonucleases. E5-CRD realized the strict recognition for both the guanine and uracil bases of dGpdUp forming Watson-Crick-type hydrogen bonds and ring stacking interactions, thus mimicking the codons of mRNAs to bind to tRNA anticodons. The docking model of E5-CRD with tRNA also suggests its substrate preference for tRNA over ssRNA. In addition, the structure of E5-CRD/dGpdUp along with the mutational analysis suggests that Arg33 may play an important role in the catalytic activity, and Lys25/Lys60 may also be involved without His in E5-CRD. Finally, the comparison of the structures of E5-CRD/dGpdUp and E5-CRD/ImmE5 (an inhibitor protein) complexes suggests that the binding mode of E5-CRD and ImmE5 mimics that of mRNA and tRNA; this may represent the evolutionary pathway of these proteins from the RNA-RNA interaction through the RNA-protein interaction of tRNA/E5-CRD.
Structural basis for sequence-dependent recognition of colicin E5 tRNase by mimicking the mRNA-tRNA interaction.,Yajima S, Inoue S, Ogawa T, Nonaka T, Ohsawa K, Masaki H Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(21):6074-82. Epub 2006 Nov 11. PMID:17099236[1]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Yajima S, Inoue S, Ogawa T, Nonaka T, Ohsawa K, Masaki H. Structural basis for sequence-dependent recognition of colicin E5 tRNase by mimicking the mRNA-tRNA interaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(21):6074-82. Epub 2006 Nov 11. PMID:17099236 doi:10.1093/nar/gkl729