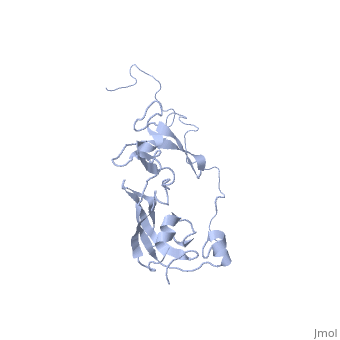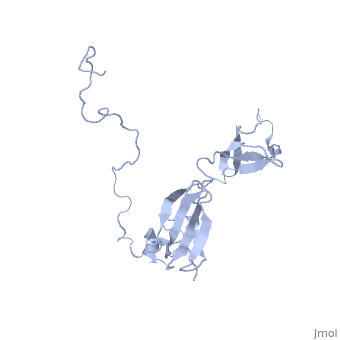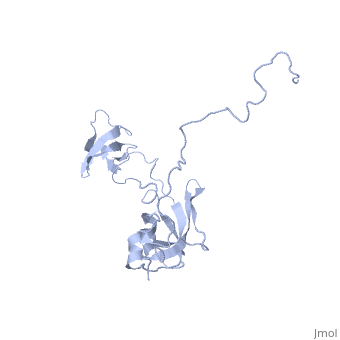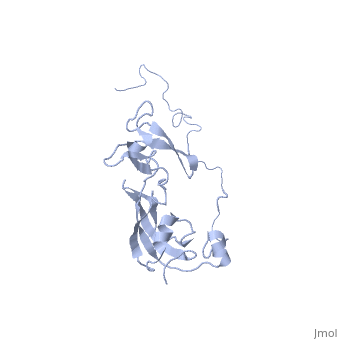| Structural highlights
Function
SLYD_ECOLI Folding helper with both chaperone and peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) activities. Chaperone activity prevents aggregation of unfolded or partially folded proteins and promotes their correct folding. PPIases catalyze the cis-trans isomerization of Xaa-Pro bonds of peptides, which accelerates slow steps of protein folding and thus shortens the lifetime of intermediates. Both strategies lower the concentration of intermediates and increase the productivity and yield of the folding reaction. SlyD could be involved in Tat-dependent translocation, by binding to the Tat-type signal of folded proteins. The PPIase substrate specificity, carried out with synthetic peptides of the 'suc-Ala-Xaa-Pro-Phe-4NA' type (where Xaa is the AA tested), was found to be Phe > Ala > Leu.[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] Required for lysis of phiX174 infected cells by stabilizing the hydrophobic viral lysis protein E and allowing it to accumulate to the levels required to exert its lytic effect. May act by a chaperone-like mechanism.[7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] Also involved in hydrogenase metallocenter assembly, probably by participating in the nickel insertion step. This function in hydrogenase biosynthesis requires chaperone activity and the presence of the metal-binding domain, but not PPIase activity.[13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18]
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
See Also
References
- ↑ Bernhardt TG, Roof WD, Young R. The Escherichia coli FKBP-type PPIase SlyD is required for the stabilization of the E lysis protein of bacteriophage phi X174. Mol Microbiol. 2002 Jul;45(1):99-108. PMID:12100551
- ↑ Zhang JW, Butland G, Greenblatt JF, Emili A, Zamble DB. A role for SlyD in the Escherichia coli hydrogenase biosynthetic pathway. J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 11;280(6):4360-6. Epub 2004 Nov 29. PMID:15569666 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M411799200
- ↑ Scholz C, Eckert B, Hagn F, Schaarschmidt P, Balbach J, Schmid FX. SlyD proteins from different species exhibit high prolyl isomerase and chaperone activities. Biochemistry. 2006 Jan 10;45(1):20-33. PMID:16388577 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi051922n
- ↑ Zhang JW, Leach MR, Zamble DB. The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase activity of SlyD is not required for maturation of Escherichia coli hydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 2007 Nov;189(21):7942-4. Epub 2007 Aug 24. PMID:17720786 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JB.00922-07
- ↑ Graubner W, Schierhorn A, Bruser T. DnaK plays a pivotal role in Tat targeting of CueO and functions beside SlyD as a general Tat signal binding chaperone. J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 9;282(10):7116-24. Epub 2007 Jan 10. PMID:17215254 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M608235200
- ↑ Weininger U, Haupt C, Schweimer K, Graubner W, Kovermann M, Bruser T, Scholz C, Schaarschmidt P, Zoldak G, Schmid FX, Balbach J. NMR solution structure of SlyD from Escherichia coli: spatial separation of prolyl isomerase and chaperone function. J Mol Biol. 2009 Mar 27;387(2):295-305. Epub 2009 Jan 27. PMID:19356587 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.01.034
- ↑ Bernhardt TG, Roof WD, Young R. The Escherichia coli FKBP-type PPIase SlyD is required for the stabilization of the E lysis protein of bacteriophage phi X174. Mol Microbiol. 2002 Jul;45(1):99-108. PMID:12100551
- ↑ Zhang JW, Butland G, Greenblatt JF, Emili A, Zamble DB. A role for SlyD in the Escherichia coli hydrogenase biosynthetic pathway. J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 11;280(6):4360-6. Epub 2004 Nov 29. PMID:15569666 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M411799200
- ↑ Scholz C, Eckert B, Hagn F, Schaarschmidt P, Balbach J, Schmid FX. SlyD proteins from different species exhibit high prolyl isomerase and chaperone activities. Biochemistry. 2006 Jan 10;45(1):20-33. PMID:16388577 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi051922n
- ↑ Zhang JW, Leach MR, Zamble DB. The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase activity of SlyD is not required for maturation of Escherichia coli hydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 2007 Nov;189(21):7942-4. Epub 2007 Aug 24. PMID:17720786 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JB.00922-07
- ↑ Graubner W, Schierhorn A, Bruser T. DnaK plays a pivotal role in Tat targeting of CueO and functions beside SlyD as a general Tat signal binding chaperone. J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 9;282(10):7116-24. Epub 2007 Jan 10. PMID:17215254 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M608235200
- ↑ Weininger U, Haupt C, Schweimer K, Graubner W, Kovermann M, Bruser T, Scholz C, Schaarschmidt P, Zoldak G, Schmid FX, Balbach J. NMR solution structure of SlyD from Escherichia coli: spatial separation of prolyl isomerase and chaperone function. J Mol Biol. 2009 Mar 27;387(2):295-305. Epub 2009 Jan 27. PMID:19356587 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.01.034
- ↑ Bernhardt TG, Roof WD, Young R. The Escherichia coli FKBP-type PPIase SlyD is required for the stabilization of the E lysis protein of bacteriophage phi X174. Mol Microbiol. 2002 Jul;45(1):99-108. PMID:12100551
- ↑ Zhang JW, Butland G, Greenblatt JF, Emili A, Zamble DB. A role for SlyD in the Escherichia coli hydrogenase biosynthetic pathway. J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 11;280(6):4360-6. Epub 2004 Nov 29. PMID:15569666 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M411799200
- ↑ Scholz C, Eckert B, Hagn F, Schaarschmidt P, Balbach J, Schmid FX. SlyD proteins from different species exhibit high prolyl isomerase and chaperone activities. Biochemistry. 2006 Jan 10;45(1):20-33. PMID:16388577 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi051922n
- ↑ Zhang JW, Leach MR, Zamble DB. The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase activity of SlyD is not required for maturation of Escherichia coli hydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 2007 Nov;189(21):7942-4. Epub 2007 Aug 24. PMID:17720786 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JB.00922-07
- ↑ Graubner W, Schierhorn A, Bruser T. DnaK plays a pivotal role in Tat targeting of CueO and functions beside SlyD as a general Tat signal binding chaperone. J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 9;282(10):7116-24. Epub 2007 Jan 10. PMID:17215254 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M608235200
- ↑ Weininger U, Haupt C, Schweimer K, Graubner W, Kovermann M, Bruser T, Scholz C, Schaarschmidt P, Zoldak G, Schmid FX, Balbach J. NMR solution structure of SlyD from Escherichia coli: spatial separation of prolyl isomerase and chaperone function. J Mol Biol. 2009 Mar 27;387(2):295-305. Epub 2009 Jan 27. PMID:19356587 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.01.034
|