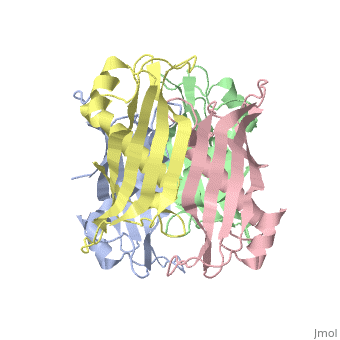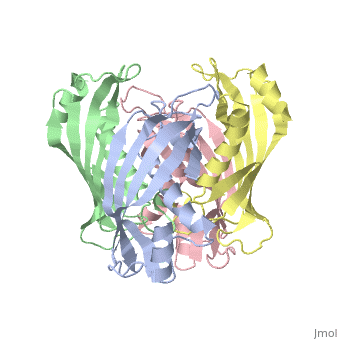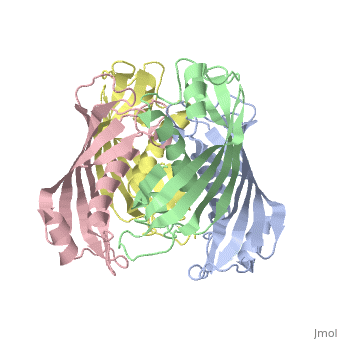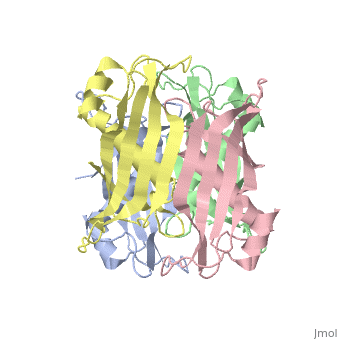
Structural highlights
Function
YBGC_HELPY Thioesterase that may be involved in phospholipid metabolism. Displays acyl-CoA thioesterase activity with lauroyl-CoA (C12:0), myristoyl-CoA (C14:0), palmitoyl-CoA (C16:0), stearoyl-CoA (C18:0) and benzoyl-CoA, catalyzing the hydrolysis of the thioester bond. Has low activity with butyryl-CoA and octanoyl-CoA.[1]
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
YbgC proteins are bacterial acyl-CoA thioesterases associated with the Tol-Pal system. This system is important for cell envelope integrity and is part of the cell division machinery. In E. coli, YbgC associates with the cell membrane and is part of a protein network involved in lipid biogenesis. In the human pathogen Helicobacter pylori, a putative homologue of YbgC, named HP0496, was found to interact with the cytotoxin CagA by two different studies. We have determined its crystal structure and characterized its enzymatic activity. The structure of HP0496 shows that it is a member of the hot-dog family of proteins, with a epsilongamma tetrameric arrangement. Finally, enzymatic assays performed with the purified protein showed that HP0496 is an acyl-CoA thioesterase that favors long-chain substrates. Proteins 2008. (c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Structural and enzymatic characterization of HP0496, a YbgC thioesterase from Helicobacter pylori.,Angelini A, Cendron L, Goncalves S, Zanotti G, Terradot L Proteins. 2008 Mar 12;72(4):1212-1221. PMID:18338382[2]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Angelini A, Cendron L, Goncalves S, Zanotti G, Terradot L. Structural and enzymatic characterization of HP0496, a YbgC thioesterase from Helicobacter pylori. Proteins. 2008 Mar 12;72(4):1212-1221. PMID:18338382 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/prot.22014
- ↑ Angelini A, Cendron L, Goncalves S, Zanotti G, Terradot L. Structural and enzymatic characterization of HP0496, a YbgC thioesterase from Helicobacter pylori. Proteins. 2008 Mar 12;72(4):1212-1221. PMID:18338382 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/prot.22014