Structural highlights
Function
S10A2_HUMAN May act as a modulator against excess calcium accumulation in normal human mammary epithelial cells. May also play a role in suppressing tumor cell growth.[1]
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
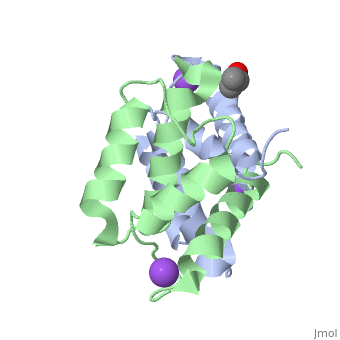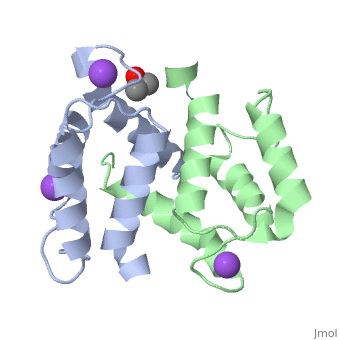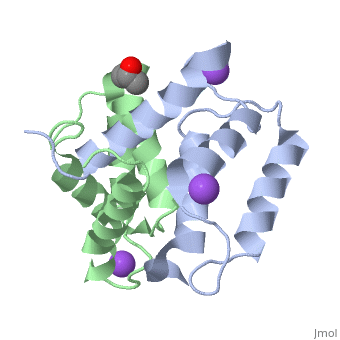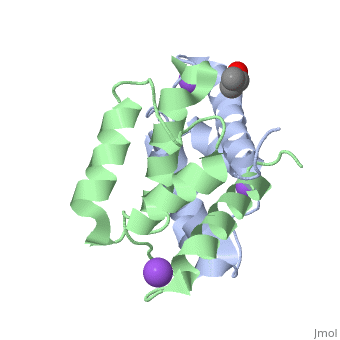
S100A2 is an EF hand-containing Ca(2+)-binding protein of the family of S100 proteins. The protein is localized exclusively in the nucleus and is involved in cell cycle regulation. It attracted most interest by its function as a tumor suppressor via p53 interaction. We determined the crystal structure of homodimeric S100A2 in the Ca(2+)-free state at 1.6-A resolution. The structure revealed structural differences between subunits A and B, especially in the conformation of a loop that connects the N- and C-terminal EF hands and represents a part of the target-binding site in S100 proteins. Analysis of the hydrogen bonding network and molecular dynamics calculations indicate that one of the two observed conformations is more stable. The structure revealed Na(+) bound to each N-terminal EF hand of both subunits coordinated by oxygen atoms of the backbone carbonyl and water molecules. Comparison with the structures of Ca(2+)-free S100A3 and S100A6 suggests that Na(+) might occupy the S100-specific EF hand in the Ca(2+)-free state.
Crystal structure of Ca2+ -free S100A2 at 1.6-A resolution.,Koch M, Diez J, Fritz G J Mol Biol. 2008 May 9;378(4):933-42. Epub 2008 Mar 19. PMID:18394645[2]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Lee SW, Tomasetto C, Swisshelm K, Keyomarsi K, Sager R. Down-regulation of a member of the S100 gene family in mammary carcinoma cells and reexpression by azadeoxycytidine treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2504-8. PMID:1372446
- ↑ Koch M, Diez J, Fritz G. Crystal structure of Ca2+ -free S100A2 at 1.6-A resolution. J Mol Biol. 2008 May 9;378(4):933-42. Epub 2008 Mar 19. PMID:18394645 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.03.019