3ecp
From Proteopedia
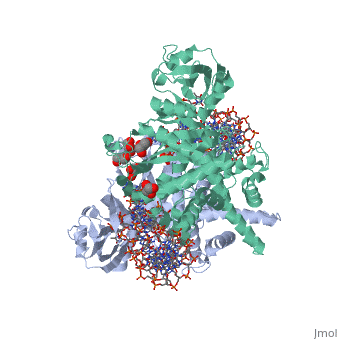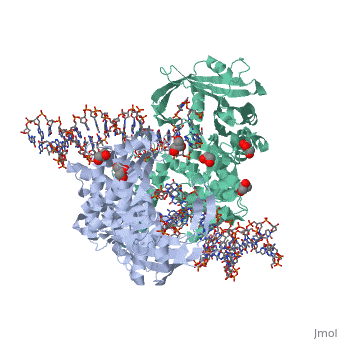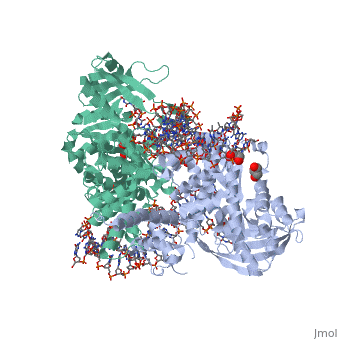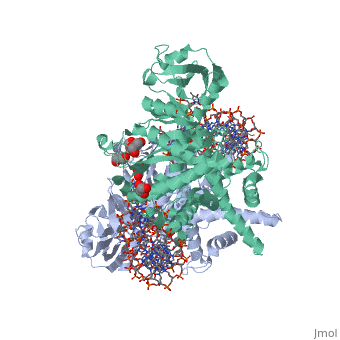
Crystal Structure Of Tn5 Transposase Complexed With 5' Phosphorylated Transposon End DNA
Structural highlights
FunctionTN5P_ECOLX Mediates transposition of transposon Tn5 by a 'cut and paste' mechanism. First, the monomeric transposase binds the 19 bp inverted DNA repeats flanking the transposon. Then, dimerization of the DNA-bound transposase creates a synaptic DNA complex. After nicking of the first DNA strand, excision of the transposon proceeds through a series of intermediates. The transposase then mediates the insertion of the transposon at a new site by strand transfer. The activity of the wild-type transposase is very low, and is further inhibited by dimerization with the transposase inhibitor (inh).[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] Evolutionary ConservationCheck, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedBacterial DNA transposition is an important model system for studying DNA recombination events such as HIV-1 DNA integration and RAG-1-mediated V(D)J recombination. This communication focuses on the role of protein-phosphate contacts in manipulating DNA structure as a requirement for transposition catalysis. In particular, the participation of the nontransferred strand (NTS) 5' phosphate in Tn5 transposition strand transfer is analyzed. The 5' phosphate plays no direct catalytic role, nonetheless its presence stimulates strand transfer approximately 30-fold. X-ray crystallography indicates that transposase-DNA complexes formed with NTS 5' phosphorylated DNA have two properties that contrast with structures formed with complexes lacking the 5' phosphate or complexes generated from in-crystal hairpin cleavage. Transposase residues R210, Y319 and R322 of the (R)YREK motif coordinate the 5' phosphate rather than the subterminal NTS phosphate, and the 5' NTS end is moved away from the 3' transferred strand end. Mutation R210A impairs the 5' phosphate stimulation. It is posited that DNA phosphate coordination by R210, Y319 and R322 results in movement of the 5' NTS DNA away from the 3'-end thus allowing efficient target DNA binding. It is likely that this role for the newly identified RYR triad is utilized by other transposase-related proteins. Phosphate coordination and movement of DNA in the Tn5 synaptic complex: role of the (R)YREK motif.,Klenchin VA, Czyz A, Goryshin IY, Gradman R, Lovell S, Rayment I, Reznikoff WS Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Oct;36(18):5855-62. Epub 2008 Sep 12. PMID:18790806[9] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
| ||||||||||||||||||||