Structural highlights
Function
HSF_KLULA DNA-binding protein that specifically binds heat shock promoter elements (HSE) and activates transcription. Also required for growth at normal temperatures.
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
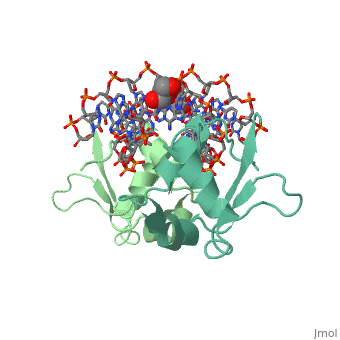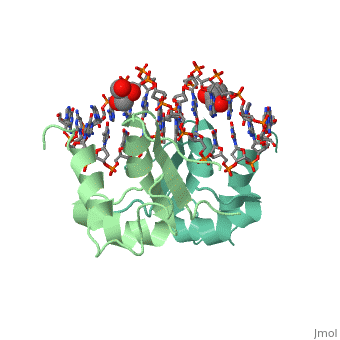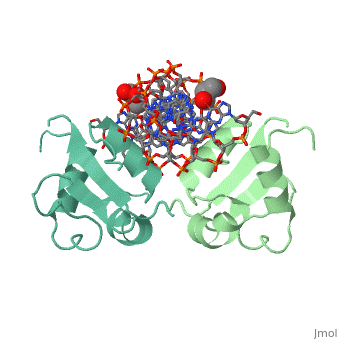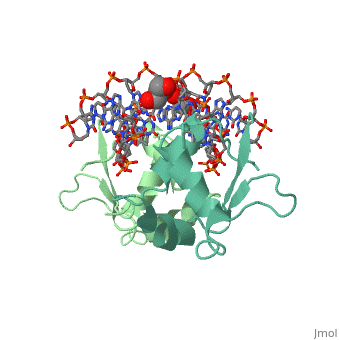
The 1.75 A crystal structure of the Kluyveromyces lactis heat shock transcription factor (HSF) DNA-binding domain (DBD) complexed with DNA reveals a protein-DNA interface with few direct major groove contacts and a number of phosphate backbone contacts that are primarily water-mediated interactions. The DBD, a 'winged' helix-turn-helix protein, displays a novel mode of binding in that the 'wing' does not contact DNA like all others of that class. Instead, the monomeric DBD, which crystallized as a symmetric dimer to a pair of nGAAn inverted repeats, uses the 'wing' to form part of the protein-protein contacts. This dimer interface is likely important for increasing the DNA-binding specificity and affinity of the trimeric form of HSF, as well as for increasing cooperativity between adjacent trimers.
A new use for the 'wing' of the 'winged' helix-turn-helix motif in the HSF-DNA cocrystal.,Littlefield O, Nelson HC Nat Struct Biol. 1999 May;6(5):464-70. PMID:10331875[1]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Littlefield O, Nelson HC. A new use for the 'wing' of the 'winged' helix-turn-helix motif in the HSF-DNA cocrystal. Nat Struct Biol. 1999 May;6(5):464-70. PMID:10331875 doi:10.1038/8269