Function
Apoptosis protease-activating factor-1 or Apoptosis peptidase-activating factor-1 (APAF-1) binds to cytochrome c and ATP to form the apoptosome which leads to the recruitment and activation of caspase 9 by cleaving the procaspase 9. Caspase 9 is involved in executing the apoptosis of cells[1].
Disease
Inactivation of Apaf-1 is implicated in disease progression and chemoresistance of some malignancies[2].
Structural highlights
Apaf-1 contains several copies of the WD-40 domain which are involved in binding to cytochrome c[3]., caspase recruitment domain (CARD) and an ATPase domain.
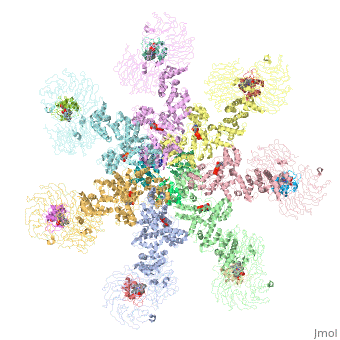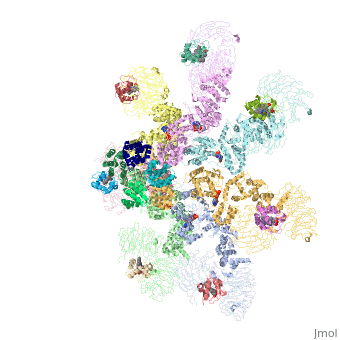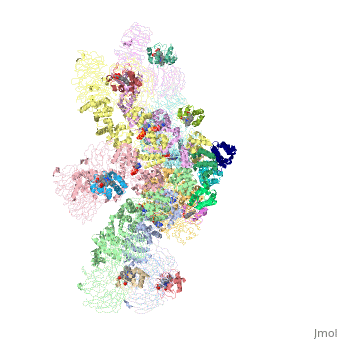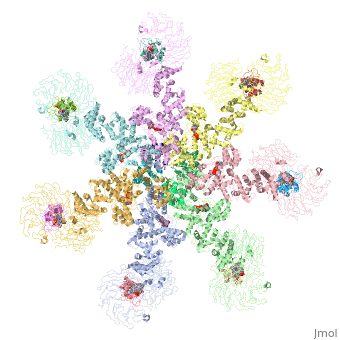
- formed by Human apoptosis protease-activating factor-1 (green; subunits A, B, C, D, E, F, G) complex with cytochrome c (red; subunits H, I, J, K, L, M, N) and caspase 9 (magenta; subunits O, P, Q, R) (PDB entry 5juy).
3D structures of apoptotic protease-activating factor-1
Apoptotic protease-activating factor-1 3D structures