Group:MUZIC:DARP
From Proteopedia

Contents |
DARP
Introduction
Diabetes related ankyrin repeat protein DARP (Ankrd23) and its two close homologs Ankrd2/Arpp and Ankrd1/CARP correspond to a conserved gene family of muscle ankyrin repeat proteins (MARPs). [1] DARP is expressed in both heart and skeletal muscle (in addition to brown fat) and was identified by its upregulation in Type 2 diabetes and insulin-resistant animals, suggesting a potential role in energy metabolism. [2]
Sequence Annotation
http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q812A3
| |||||||||
| 1n0r, resolution 1.50Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | |||||||||
| Related: | 1n0q | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBsum, RCSB | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
Structure
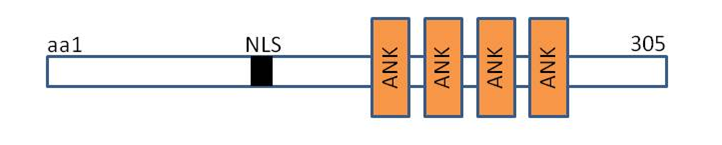
DARP contains putative nuclear localization signals,four tandem ankyrin-like repeats, potential coiled-coil dimerization motif within its unique aminoterminal domain that mediates the formation of homodimers. [3] The amino acid sequence of DARP showed high similarity to cardiac ankyrin-repeat protein (CARP) and ankyrin-repeat domain 2 (Ankrd2) with 45 and 36% identities, respectively.Silico analysis of promoter of DARP gene indicated the existence of binding site for PPARγ consensus sequence recognised by PPARγ is positioned upstream of transcriptional start site in the DARP gene from -18495 to -18517 base pair.[3]
Gene Function and Interactions
DARP knock out muscle fibers were less stiff, tended to have longer resting sarcomere lengths, and expressed a longer isoform of titin than their wild-type counterparts,indicating that this protein may play a role in the passive mechanical behavior of muscle. [4] DARP expression is altered by a change of energy supply and energy metabolic condition, induced by excess fatty acid treatment in vitro and fasting in vivo. [2] The expression of DARP is induced during recovery following starvation. In cultured fetal rat cardiac myocytes, passive stretch induced differential distribution patterns of DARP: staining for DARP was increased in the nucleus, at the I-band region of myofibrils and also at intercalated discs. [1] Differently from its homolog genes, DARP is not upregulated after ECs.[5] DARP interacts with a tyrosine-rich binding motif between Ig80 and Ig81 of titin and with myopalladin. [1]
Pathology
Its altered expression in transgenic mice with increased or decreased PI3K(p110α) activity has a significant impact on functionality of the Z-disc and,subsequently,cardiac function.PI3K(p110α) protects the heart against myocardial infarction. Together with other genes encoding muscle structural/associated proteins, such as dystroglycan (Dag1), filamin C(Flnc), Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 2(Rock2), crystallin, α B (Cryab), Cd151, integrin β 1 binding protein 2(Itgb1bp2/melusin), Lim domain binding 3(Ldb3/cypher), and synaptopodin 2 (Synpo2/myopodin), DARP/Ankrd23 was found up-and down-regulated respectively in the caPI3K (consitutively active PI3K)and dnPI3K(dominant negative PI3K.[6] DARP,calpain-10 and calpain-3 play an important role in the regulation of glucose utilization in skeletal muscle. Calpain-3 activity may be regulated by DARP.[1]