Group:MUZIC:Tritopodin
From Proteopedia

Contents |
Synaptopodin 2-like protein / Tritopodin
Introduction
The synaptopodin 2-like protein or tritopodin is the third member (besides myopodin and synaptopodin) of the podin protein family and is encoded by the gene SYNPO2L[1]. Tritopodin has been revealed by database searches, and since it is the third member of the podin family of proteins with extended sequence similarity, was named ‘‘tritopodin’’. Tritopodin is also known under the names synaptopodin 2-like, myopodin-like and CHAP (cytoskeletal heart-enriched actin-associated protein) and is found in heart and skeletal muscle tissue [1].
Sequence Annotation
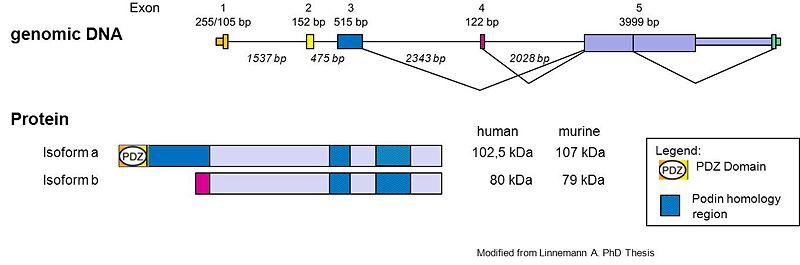
Tritopodin shares 33% homology at the aminoacid level with myopodin and 30% with Synaptopodin [2], which predicts similar functions for both proteins. The human gene SYNPO2L, that encodes tritopodin exists of 5 exons, which are separated by different large introns. Database analysis (UCSC Genome Browser, EMBL) predicted 2 putative differential isoforms. Splicing isoforms: Tritopodin a (in human 102.5kDa and in mouse 103.3kDa and Tritopodin b (in both human and mouse 79kDa) (see figure). After done biochemicals experiments, Beqqali et al. postulated 2 isoforms: mCHAPa from exon 1,2,3 and 5, as well as mCHAPb that result from a start-codon in exon 4, from which derives two proteins variants of 140kDa (mCHAPa) and 110kDa (mCHAPb) [3].
Function
Tritopodin is expressed in vivo and in vitro in differentiated skeletal- and heart muscle cells, and is conserved amongst vertebrates, indicating an essential role in muscle function. Furthermore Tritopodin is able to translocate to the nucleus, and plays an important role in skeletal and cardiac muscle development. [4] [5].
Tritopodin Interactions
Tritopodin localize in the sarcomeric Z-disc, where interact with α-actinin, which was verified by CoIPs and yeast two-hybrid assays [6]. In adult skeletal and cardiac muscle tissue from mCHAP was demonstrated the colocalization with α-actinin in the sarcomeric Z-disc and in the nucleus in embryonal cardiomyocytes [7].
Pathology
Knockdown of CHAP in zebrafish, results in aberrant heart and skeletal muscle development, disorganized sarcomeres and ultimately lead to diminished cardiac contractility.
References
- ↑ Claeys KG, van der Ven PF, Behin A, Stojkovic T, Eymard B, Dubourg O, Laforet P, Faulkner G, Richard P, Vicart P, Romero NB, Stoltenburg G, Udd B, Fardeau M, Voit T, Furst DO. Differential involvement of sarcomeric proteins in myofibrillar myopathies: a morphological and immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol. 2009 Mar;117(3):293-307. Epub 2009 Jan 17. PMID:19151983 doi:10.1007/s00401-008-0479-7
- ↑ Mundel P, Heid HW, Mundel TM, Kruger M, Reiser J, Kriz W. Synaptopodin: an actin-associated protein in telencephalic dendrites and renal podocytes. J Cell Biol. 1997 Oct 6;139(1):193-204. PMID:9314539
- ↑ Beqqali A, Monshouwer-Kloots J, Monteiro R, Welling M, Bakkers J, Ehler E, Verkleij A, Mummery C, Passier R. CHAP is a newly identified Z-disc protein essential for heart and skeletal muscle function. J Cell Sci. 2010 Apr 1;123(Pt 7):1141-50. Epub 2010 Mar 9. PMID:20215401 doi:10.1242/jcs.063859
- ↑ Linnemann A, van der Ven PF, Vakeel P, Albinus B, Simonis D, Bendas G, Schenk JA, Micheel B, Kley RA, Furst DO. The sarcomeric Z-disc component myopodin is a multiadapter protein that interacts with filamin and alpha-actinin. Eur J Cell Biol. 2010 Sep;89(9):681-92. Epub 2010 May 31. PMID:20554076 doi:10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.04.004
- ↑ Beqqali A, Monshouwer-Kloots J, Monteiro R, Welling M, Bakkers J, Ehler E, Verkleij A, Mummery C, Passier R. CHAP is a newly identified Z-disc protein essential for heart and skeletal muscle function. J Cell Sci. 2010 Apr 1;123(Pt 7):1141-50. Epub 2010 Mar 9. PMID:20215401 doi:10.1242/jcs.063859
- ↑ Linnemann A, van der Ven PF, Vakeel P, Albinus B, Simonis D, Bendas G, Schenk JA, Micheel B, Kley RA, Furst DO. The sarcomeric Z-disc component myopodin is a multiadapter protein that interacts with filamin and alpha-actinin. Eur J Cell Biol. 2010 Sep;89(9):681-92. Epub 2010 May 31. PMID:20554076 doi:10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.04.004
- ↑ Beqqali A, Monshouwer-Kloots J, Monteiro R, Welling M, Bakkers J, Ehler E, Verkleij A, Mummery C, Passier R. CHAP is a newly identified Z-disc protein essential for heart and skeletal muscle function. J Cell Sci. 2010 Apr 1;123(Pt 7):1141-50. Epub 2010 Mar 9. PMID:20215401 doi:10.1242/jcs.063859