Group:MUZIC:XIN
From Proteopedia

Xin actin-binding repeat-containing protein 1
Introduction
Xin actin-binding repeat-containing protein 1 (Alternative names: Cardiomyopathy-associated protein 1, CMYA1, XIN, mXinα) is coded by the gene (Synonyms:CMYA1, XIN) and has an actin-binding domain (ABD). It crosslinks actin filaments and participates in anchoring of membrane proteins. Intraexogic splicing leads to a least three different isoforms (XinA, XinB, XinC).
Contents |
Sequence Annotation
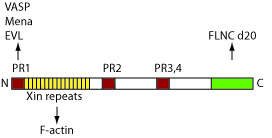
The largest isoform of Xin actin-binding repeat-containing protein 1, XinA comprises 1843 amino acids and is divided in several domains.At the N-terminus there is proline-rich region including an EVH1 domain-binding consensus motif, which is shown to be functional in binding type I EVH1 domains of the members of the Ena/VASP protein family[1]. The following Xin repeats domain consists of 16 copies of the 16 aa-comprising consensus sequence and can bind to F-actin. This domain is followed by the proline-rich region 2,3,4 containing SH3 domain binding motifs. At the C-terminus there is filamin C-specific binding site (FBS)[1].No high resolution structures are available. Cherepanova O. et al discuss conducted EM-studies on Xin-repeats binding to F-actin. [2] Xirp2 encoded by the gene CMYA3 comprisis also Xin-Repeats. UNIPROT (XIRP1_HUMAN) UNIPROT (XIRP2_HUMAN)
Figure 1: Schematic overview of XinA. Depicted in red are the prolin-reach (PR) domains 1,2,3 and 4. In yellow the Xin-repeat domain is shown and in green the filamin C-specific binding site.
Function and Interactions
Xin localizes at intercalated discs (ICD, structure at the end of the myocytes that transduce force from the myofibrils via the cell membranes to the extracelluar matrix and neighboring cells) in the adult heart and at the myotendinous junction (MTJ) of skeletal muscle tissue.
Xin and Mena/VASP colocalize with filamin c in ICDs. It has been shown that Xin directly binds the EVH1 domain proteins Mena and VASP[1], the unique insertion containing Ig domain 20[1] and directly binds F-actin [3].
Pathology
Knock out of all Xin isoforms in mice generates only a mild cardiac phenotype. Wanq Q. et al. review Xin repeat-containing proteins and how this protein family promotes ICD maturation and stability for normal cardiac function[4].
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 van der Ven PF, Ehler E, Vakeel P, Eulitz S, Schenk JA, Milting H, Micheel B, Furst DO. Unusual splicing events result in distinct Xin isoforms that associate differentially with filamin c and Mena/VASP. Exp Cell Res. 2006 Jul 1;312(11):2154-67. Epub 2006 Apr 24. PMID:16631741 doi:S0014-4827(06)00110-8
- ↑ Cherepanova O, Orlova A, Galkin VE, van der Ven PF, Furst DO, Jin JP, Egelman EH. Xin-repeats and nebulin-like repeats bind to F-actin in a similar manner. J Mol Biol. 2006 Feb 24;356(3):714-23. Epub 2005 Dec 13. PMID:16384582 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.11.082
- ↑ Pacholsky D, Vakeel P, Himmel M, Lowe T, Stradal T, Rottner K, Furst DO, van der Ven PF. Xin repeats define a novel actin-binding motif. J Cell Sci. 2004 Oct 15;117(Pt 22):5257-68. Epub 2004 Sep 28. PMID:15454575 doi:10.1242/jcs.01406
- ↑ Wang Q, Lin JL, Wu KH, Wang DZ, Reiter RS, Sinn HW, Lin CI, Lin CJ. Xin proteins and intercalated disc maturation, signaling and diseases. Front Biosci. 2012 Jun 1;17:2566-93. PMID:22652799