We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Myosin light chain kinase
From Proteopedia
| |||||||||||
3D structures of MLCK
Updated on 05-November-2019
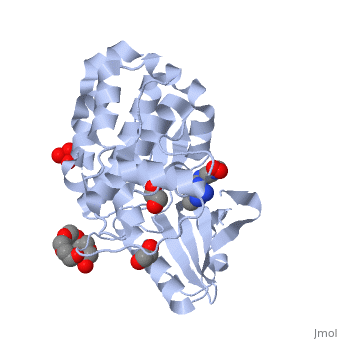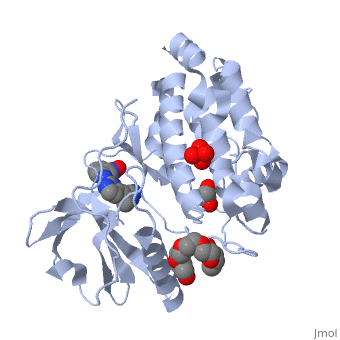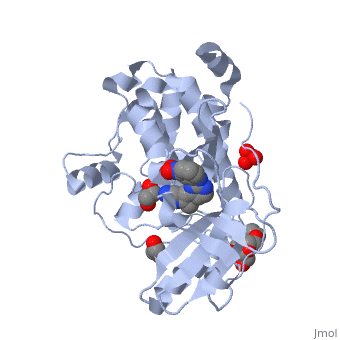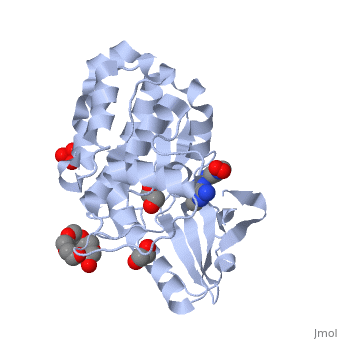
2x4f – hMLCK residues 40-388 - human
6c6m - hMLCK 3rd Ig-like domain residues 405-507
2yr3 - hMLCK 4th Ig-like domain residues 510-601 – NMR
2cqv – hMLCK 8th Ig-like domain residues 1238-1338 – NMR
References
- ↑ Stull JT, Tansey MG, Tang DC, Word RA, Kamm KE. Phosphorylation of myosin light chain kinase: a cellular mechanism for Ca2+ desensitization. Mol Cell Biochem. 1993 Nov;127-128:229-37. PMID:7935354
- ↑ Flores C, Ma SF, Maresso K, Ober C, Garcia JG. A variant of the myosin light chain kinase gene is associated with severe asthma in African Americans. Genet Epidemiol. 2007 May;31(4):296-305. PMID:17266121 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/gepi.20210
- ↑ Clayburgh DR, Barrett TA, Tang Y, Meddings JB, Van Eldik LJ, Watterson DM, Clarke LL, Mrsny RJ, Turner JR. Epithelial myosin light chain kinase-dependent barrier dysfunction mediates T cell activation-induced diarrhea in vivo. J Clin Invest. 2005 Oct;115(10):2702-15. Epub 2005 Sep 22. PMID:16184195 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI24970