We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Paired box protein
From Proteopedia
| |||||||||||
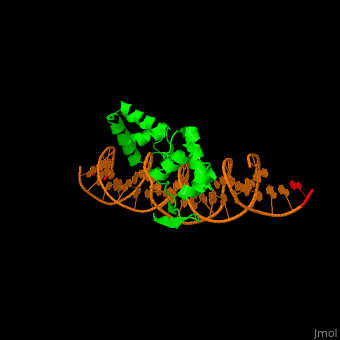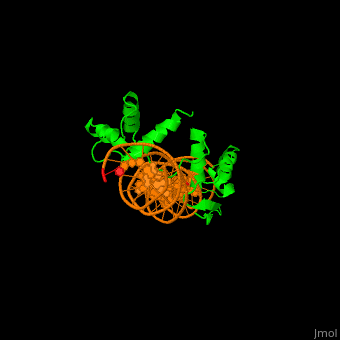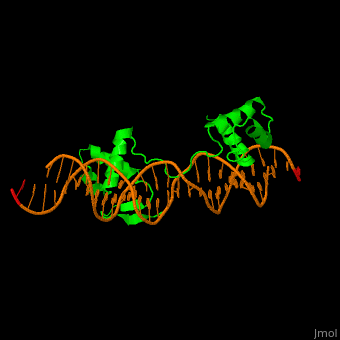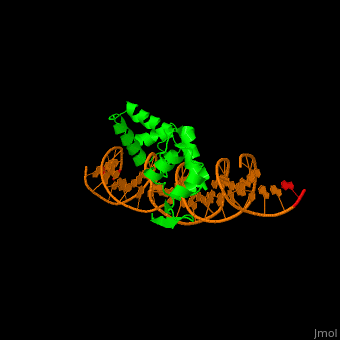
3D Structures of paired box protein
Updated on 17-September-2020
References
- ↑ Thompson KW, Joshi P, Dymond JS, Gorrepati L, Smith HE, Krause MW, Eisenmann DM. The Paired-box protein PAX-3 regulates the choice between lateral and ventral epidermal cell fates in C. elegans. Dev Biol. 2016 Apr 15;412(2):191-207. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.03.002. Epub 2016, Mar 4. PMID:26953187 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.03.002
- ↑ Ferretti E, Arturi F, Mattei T, Scipioni A, Tell G, Tosi E, Presta I, Morisi R, Lacroix L, Gulino A, Russo D, Damante G, Filetti S. Expression, regulation, and function of paired-box gene 8 in the human placenta and placental cancer cell lines. Endocrinology. 2005 Sep;146(9):4009-15. Epub 2005 Jun 16. PMID:15961562 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1210/en.2005-0084
- ↑ Li G, Xu F, Zhu J, Krawczyk M, Zhang Y, Yuan J, Patel S, Wang Y, Lin Y, Zhang M, Cai H, Chen D, Zhang M, Cao G, Yeh E, Lin D, Su Q, Li WW, Sen GL, Afshari N, Chen S, Maas RL, Fu XD, Zhang K, Liu Y, Ouyang H. Transcription Factor PAX6 (Paired Box 6) Controls Limbal Stem Cell Lineage in Development and Disease. J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 14;290(33):20448-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.662940. Epub, 2015 Jun 4. PMID:26045558 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.662940
- ↑ Baldwin CT, Lipsky NR, Hoth CF, Cohen T, Mamuya W, Milunsky A. Mutations in PAX3 associated with Waardenburg syndrome type I. Hum Mutat. 1994;3(3):205-11. PMID:8019556 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/humu.1380030306