We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
PleD activation
From Proteopedia
Contents |
Activation via dimerization
Activation of PleD proceeds via phosphorylation-induced dimerization. Upon modification of Asp53 of the Rec domain, the intramolecular packing of the Rec and Rec' domains is changed. This in turn, reduces the Kd of dimerization considerably, because the dimerization interface of the (Rec-Rec')2 "stem" is improved.
Stem mediated dimerization enhances diguanylate cyclase efficiency, because it favors formation of the catalytically competent (GGDEF)2 dimer (not shown here , but see back, bottom of page).
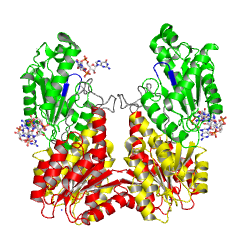
non-active state
|
monomer in solution, in the crystal
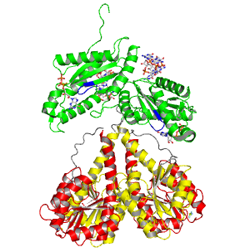
activated state
|
to mimick phosphorylation, in the crystal
References
Non-activated PleD structure 1w25:
- Chan C, Paul R, Samoray D, Amiot NC, Giese B, Jenal U, Schirmer T. Structural basis of activity and allosteric control of diguanylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Dec 7;101(49):17084-9. Epub 2004 Nov 29. PMID:15569936
Activated PleD structure 2v0n:
- Wassmann P, Chan C, Paul R, Beck A, Heerklotz H, Jenal U, Schirmer T. Structure of BeF3- -modified response regulator PleD: implications for diguanylate cyclase activation, catalysis, and feedback inhibition. Structure. 2007 Aug;15(8):915-27. PMID:17697997 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2007.06.016