User:Alexandra Helleux/Sandbox1138
From Proteopedia
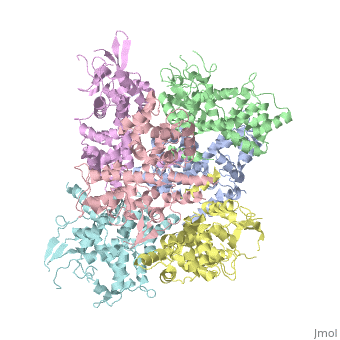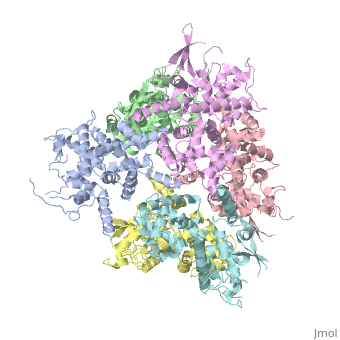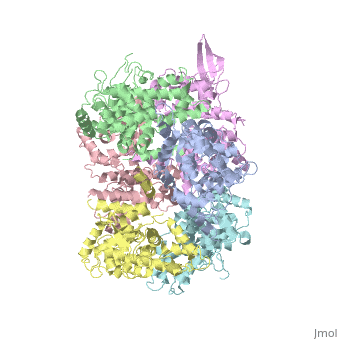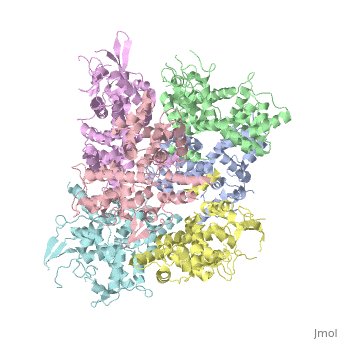
Structure of MICU1
MICU 1 (Mitochondrial Calcium Uptake 1) is a key regulator of mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) required to increase calcium uptake by MCU when cytoplasmic calcium concentration is high.Calcium is involved in signalling pathways in cells and because of that it plays a lot of important roles throughout the body (muscle contraction, cell growth, cell movement...) It also regulates glucose-dependent insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells by regulating mitochondrial calcium uptake.
HistoryMICU1 was identified as an essential element of mitochondrial calcium uptake in 2010. It was crystalised in the presence of calcium chloride and methyl-pentanediol (MPD). The recent discovery of this protein doesn’t permit to have more information about its evolutionary conservation. FunctionMICU 1 is a regulator of Ca 2+ uptakes in mitochondria. To do this regulation, it can sense the concentration of calcium in the cytosol of the cell thanks to 2 EF-hand domains. It mainly acts on MCU which is a transmembrane uniporter channel located on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. To interact with MCU, MICU1 has to be linked to MICU2 (a paralogue protein). The entire complex of Ca2+ regulation is MICU1/MICU2/MCU/EMRE. EMRE is a protein which is required for the interaction of MCU with MICU1/MICU2. When it is not linked to Ca2+ it has an hexameric conformation. In this conformation MICU 1 silences the activity of MCU/EMRE and stop the Ca 2+ from entering the mitochondria by blocking the entrance of the channel. When there is a lot of calcium in the intermembrane and so in the cytoplasm, Ca2+ binds to MICU1, then it changes its conformation and separates into multiple homooligomers. This leads to the opening of the “gate” in front of the MCU channel, letting the calcium enter into the matrix. Structural highlightsMICU 1 is a ~54kDa transmembrane protein composed by an amino-terminal mitochondrial targeting sequence, a transmembrane helix and a cytosolic C-terminus which contain different important domains described after. In absence of Ca2+, MICU1 is an homohexamer with a composed by several alpha helix (in pink), beta sheets (in orange), turns (in purple) and loops (in white). When it , it becomes a . MICU 1 is composed by differents domains :
DiseaseIf MICU1 gene is modified, Ca2+ can be load in higher concentration in the mitochondry resulting Myopathy with extrapyramidal signs (MPXPS). This is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by early-onset proximal muscle weakness with a static course and moderately to grossly elevated serum creatine kinase levels accompanied by learning difficulties. Most patients develop subtle extrapyramidal motor signs that progress to a debilitating disorder of involuntary movement with variable features, including chorea, tremor, dystonic posturing and orofacial dyskinesia. Additional variable features include ataxia, microcephaly, ophthalmoplegia, ptosis, optic atrophy and axonal peripheral neuropathy. See also
References | ||||||||||||||||||||||