User:Luis Netto/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
Ohr
Ohr (Organic Hydroperoxide Resistance Protein)1zb8 is a Cys based peroxidase [1],[2] that display higher preference for hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) than for organic hydroperoxides. Accordingly, bacteria with the gene for Ohr deleted displayed increased sensitivity for organic hydroperoxides but not for hydrogen peroxide [3].
FunctionOhr is a Cys based peroxidase that means the active site Cys is very reactive towards organic hydroperoxides. This high reactivity is achieved in the active site by interactions with fully conserved Arg and Glu residues among others
Diseaserelated with relevance
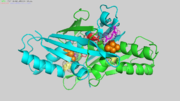
RelevanceOxidants such as fatty acid hydroperoxides are signaling molecules involved in host-pathogen interactions, and therefore, their levels are strictly controlled by peroxidases and other mechanisms [1±4]. Ohr (Organic hydroperoxide resistance) proteins are Cys-based, dithiol-dependent peroxidases that display unique biochemical and structural properties [5,6]. Ohr enzymes play central roles in the bacterial response to peroxynitrite and fatty acid hydroperoxides, two oxidants involved in host±pathogen interactions [1]. These enzymes are found in bacteria and fungi, and they are absent in their hosts (plants and animals) [7], making them promising targets for drug discovery. Some examples of pathogenic bacteria that express Ohr proteins are Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Vibrio cholerae and Xyllela fastidiosa [7]. Xylella fastidiosa is a plant pathogen with agronomic interest, causing disease in citrus, grapes and olives [8]. Structural highlightsOhr is a homo-dimer, with a symmetrical,oval shape. The two monomers are tightly wrapped around each other in a head-to-tail orientation to generate a compact quaternary structure (Figure 1).
In Figure 1, one monomer is depicted in light blue the other in green. Reactive Cys also called peroxidatic Cys (Cp) is depicted in orange. Catalytic Arg (red) and Glu (pink) compose the catalytic triad with Cp. The catalytic Glu orientates the catalytic Arg towards Cp, increasing its nucleophilicity.
Arg19 and Glu 50 of one chain (lets say chain A) compose the triad with Cys61 of the other chain (in this case chain B).
The structures of Ohr in the reduced and oxidized form were also obtained. For Ohr from Xylella fastidiosa the structures of both reduced and oxidized are available.
References
| ||||||||||||