Publication Abstract from PubMed
Nucleotide excision repair is distinguished from other DNA repair pathways by its ability to process a wide range of structurally unrelated DNA lesions. In bacteria, damage recognition is achieved by the UvrA.UvrB ensemble. Here, we report the structure of the complex between the interaction domains of UvrA and UvrB. These domains are necessary and sufficient for full-length UvrA and UvrB to associate and thereby form the DNA damage-sensing complex of bacterial nucleotide excision repair. The crystal structure and accompanying biochemical analyses suggest a model for the complete damage-sensing complex.
A structural model for the damage-sensing complex in bacterial nucleotide excision repair., Pakotiprapha D, Liu Y, Verdine GL, Jeruzalmi D, J Biol Chem. 2009 May 8;284(19):12837-44. Epub 2009 Mar 13. PMID:19287003
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
About this Structure
3fpn is a 2 chains structure of sequences from Geobacillus stearothermophilus. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
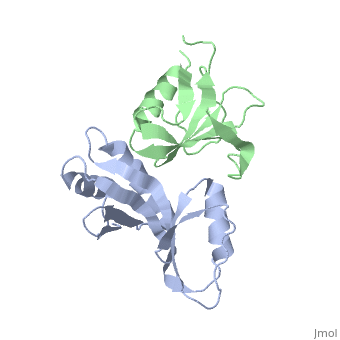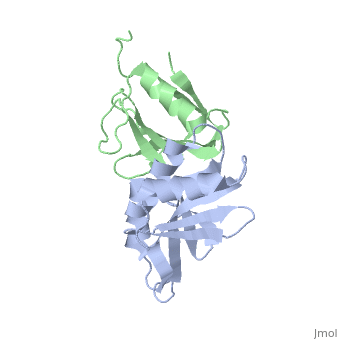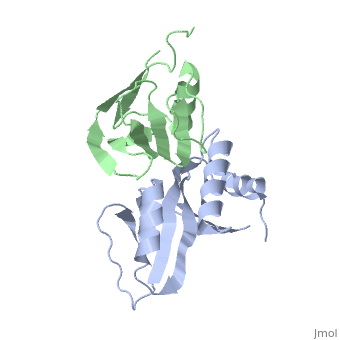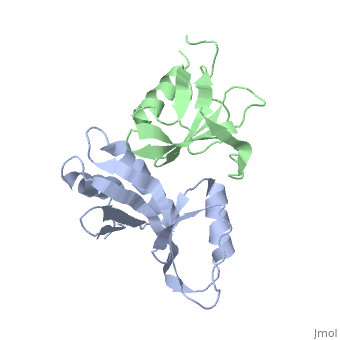
to Figure 3A of the paper describing this structure. .
[Note: the following view generates a substantial surface which may take a minute or so to calculate.].
to Figure 3B of the paper describing this structure.
. [If the animation seems to be stuck, scroll in the bar on the right of your browser. This is an approximation of the information conveyed in the figure in the manuscript.]
to Figure 3B of the paper describing this structure.
. [If the animation seems to be stuck, scroll in the bar on the right of your browser. This is an approximation of the information conveyed in the figure in the manuscript.]