We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
VlsE
From Proteopedia
| |||||||||||
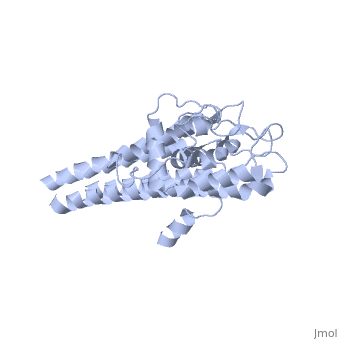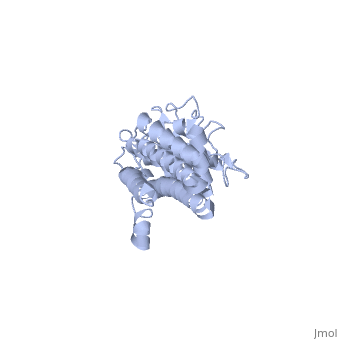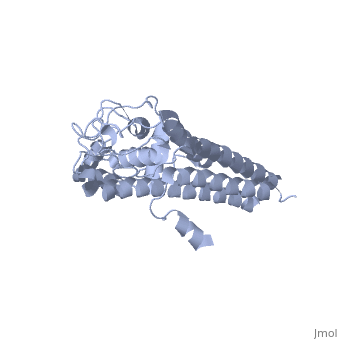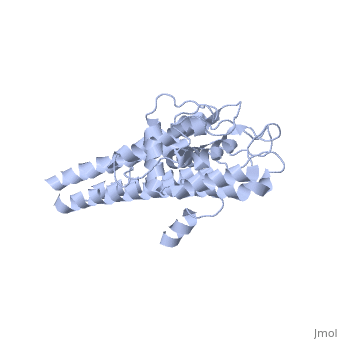
3D structures of VlsE
Updated on 16-January-2019
1l8w – VlsE – Borrelia burgdorferi
See also SB2013 L04gr5
Notes
- References are cited once per section due to technical difficulties. Please note that references are referred to more than once per section because of this error.
Additional Links
References
- ↑ Lo Re V 3rd, Occi JL, MacGregor RR. Identifying the vector of Lyme disease. Am Fam Physician. 2004 Apr 15;69(8):1935-7. PMID:15117014
- ↑ Eicken C, Sharma V, Klabunde T, Lawrenz MB, Hardham JM, Norris SJ, Sacchettini JC. Crystal structure of Lyme disease variable surface antigen VlsE of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 14;277(24):21691-6. Epub 2002 Mar 28. PMID:11923306 doi:10.1074/jbc.M201547200
- ↑ Liang FT, Philipp MT. Analysis of antibody response to invariable regions of VlsE, the variable surface antigen of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1999 Dec;67(12):6702-6. PMID:10569796
- ↑ Eicken C, Sharma V, Klabunde T, Lawrenz MB, Hardham JM, Norris SJ, Sacchettini JC. Crystal structure of Lyme disease variable surface antigen VlsE of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 14;277(24):21691-6. Epub 2002 Mar 28. PMID:11923306 doi:10.1074/jbc.M201547200
- ↑ Liang FT, Philipp MT. Analysis of antibody response to invariable regions of VlsE, the variable surface antigen of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1999 Dec;67(12):6702-6. PMID:10569796
- ↑ Liang FT, Philipp MT. Analysis of antibody response to invariable regions of VlsE, the variable surface antigen of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1999 Dec;67(12):6702-6. PMID:10569796
- ↑ Eicken C, Sharma V, Klabunde T, Lawrenz MB, Hardham JM, Norris SJ, Sacchettini JC. Crystal structure of Lyme disease variable surface antigen VlsE of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 14;277(24):21691-6. Epub 2002 Mar 28. PMID:11923306 doi:10.1074/jbc.M201547200
- ↑ Zhang J and Norris S. 1998. Genetic Variation of the Borrelia burgdorferi’’ Gene vlsE Involves Cassette-Specific, Segmental Gene Conversion. Infection and Immunity. 66(8): 3698–3704
- ↑ Sung S, McDowell J, and Marconi R. 2001. Evidence for the Contribution of Point Mutations to vlsE Variation and for Apparent Constraints on the Net Accumulation of Sequence Changes in vlsE during Infection with Lyme Disease Spirochetes. Journal of Bacteriology183(20): 5855–5861.
- ↑ Anguita J, Thomas V, Samanta S, Persinski R, Hernanz C, Barthold SW, Fikrig E. Borrelia burgdorferi-induced inflammation facilitates spirochete adaptation and variable major protein-like sequence locus recombination. J Immunol. 2001 Sep 15;167(6):3383-90. PMID:11544329
- ↑ Liang FT, Philipp MT. Analysis of antibody response to invariable regions of VlsE, the variable surface antigen of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1999 Dec;67(12):6702-6. PMID:10569796
- ↑ Liang FT, Aberer E, Cinco M, Gern L, Hu CM, Lobet YN, Ruscio M, Voet PE Jr, Weynants VE, Philipp MT. Antigenic conservation of an immunodominant invariable region of the VlsE lipoprotein among European pathogenic genospecies of Borrelia burgdorferi SL. J Infect Dis. 2000 Nov;182(5):1455-62. Epub 2000 Oct 9. PMID:11023468 doi:10.1086/315862
- ↑ Eicken C, Sharma V, Klabunde T, Lawrenz MB, Hardham JM, Norris SJ, Sacchettini JC. Crystal structure of Lyme disease variable surface antigen VlsE of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 14;277(24):21691-6. Epub 2002 Mar 28. PMID:11923306 doi:10.1074/jbc.M201547200
- ↑ Eicken C, Sharma V, Klabunde T, Lawrenz MB, Hardham JM, Norris SJ, Sacchettini JC. Crystal structure of Lyme disease variable surface antigen VlsE of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 14;277(24):21691-6. Epub 2002 Mar 28. PMID:11923306 doi:10.1074/jbc.M201547200
- ↑ Chandra A, Latov N, Wormser GP, Marques AR, Alaedini A. Epitope mapping of antibodies to VlsE protein of Borrelia burgdorferi in post-Lyme disease syndrome. Clin Immunol. 2011 Oct;141(1):103-10. Epub 2011 Jul 2. PMID:21778118 doi:10.1016/j.clim.2011.06.005
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Jessica M Svoboda, Christine Paulose, Cindy Lee, Alexander Berchansky, Jaime Prilusky, Lukas Klees