High mobility group protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: <StructureSection load='2gzk' size='340' side='right' caption='Rat HMG1 tandem boxes complexed with DNA (PDB code 2gzk).' scene=''> '''High mobility group protein (HMG)''' is a chroma...) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
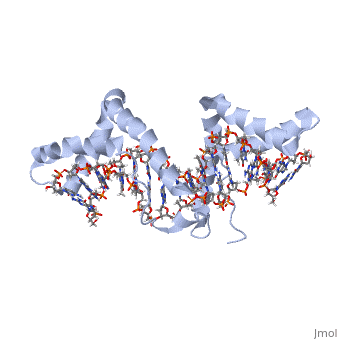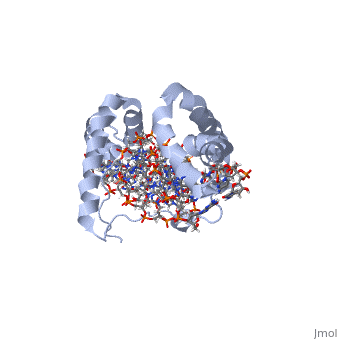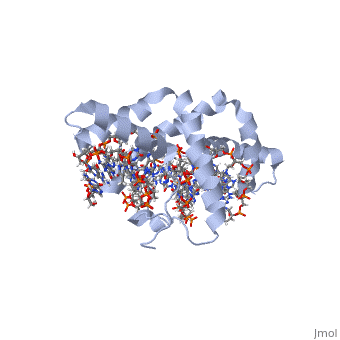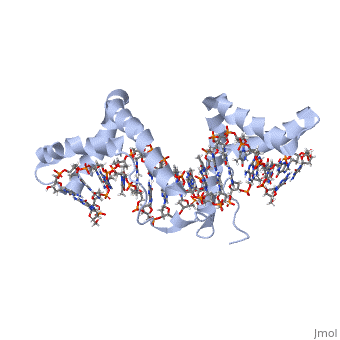
| - | + | <StructureSection load='2gzk' size='340' side='right' caption='Rat HMGB1 tandem boxes complexed with DNA (PDB code [[2gzk]]).' scene=''> | |
| - | <StructureSection load='2gzk' size='340' side='right' caption='Rat | + | |
| - | + | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| + | '''High mobility group protein (HMG)''' is a chromatin protein which organizes the DNA and regulates transcription. HMG superfamilies differ by their DNA-binding domains.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''HMGA'''s bind via an AT-hook domain. For details on HMGA see [[HMGI(Y)]].<br /> | ||
| + | * '''HMGB'''s bind via box domain<ref>PMID:17979838</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''HMGN'''s bind via a nucleosome binding domain.<br /> | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| + | Rearrangements of the HMGA2 gene were detected in human benign lipoma tumors<ref>PMID:11576996</ref>. | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| + | Overexpression of HMGB1 is associated with cancer and is targeted for cancer therapy<ref>PMID:20123075</ref>. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 19: | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| + | |||
| + | *HMGA | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[2ezd]], [[2eze]], [[2ezf]], [[2ezg]] – hHMG-1 + DNA - human<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *HMGB box 1 domain residues 1-84; tandem boxes domain residues 1-166 | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[2yrq]] – hHMG-1 tandem boxes - human - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2rtu]] – hHMG-1 box 1 - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2ly4]] – hHMG-1 box domain + cellular tumor antigen p53 - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6cij]], [[6cik]], [[6cil]], [[6cim]] – hHMG-1 tandem boxes + RAG-1 + RAG-2 + DNA<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6cg0]], [[6oem]], [[6oen]] – hHMG-1 tandem boxes + RAG-1 + RAG-2 + DNA – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[8i9m]] – hHMG-1 89-183 + RAGE – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[9cg9]] – hHMG-1 + nucleosome – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2eqz]], [[2yqi]] – hHMG-3 box domain - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1j3d]] – pHMG-2 C terminal – pig - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1j3c]] – pHMG-2 C terminal (mutant) - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1j3x]] – pHMG-2 N terminal (mutant) - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1hme]], [[1hmf]] – rHMG-1 B domain – rat - NMR <br /> | ||
| + | **[[1aab]] – rHMG-1 A domain - NMR <br /> | ||
| + | **[[1ckt]], [[4qr9]] – rHMG-1 A domain + DNA <br /> | ||
| + | **[[2gzk]] – rHMG-1 tandem boxes + DNA <br /> | ||
| + | **[[5zdz]], [[5ze0]], [[5ze1]], [[5ze2]] – mHMG-1 tandem boxes + RAG-1 + RAG-2 + DNA – mouse<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6oeo]], [[6oer]] – mHMG-1 tandem boxes + RAG-1 + RAG-2 + DNA – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1hsm]], [[1hsn]], [[1nhm]], [[1nhn]] – HMG-1 box domain – chinese hamster - NMR <br /> | ||
| + | **[[1hma]] – DmHMG-D DNA-binding domain – ''Drosophila melanogaster'' - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1qrv]] – DmHMG-D DNA-binding domain + DNA <br /> | ||
| + | **[[3nm9]] – DmHMG-D DNA-binding domain (mutant) + DNA <br /> | ||
| + | **[[8r1x]] – DmHMG-D DNA-binding domain + DNA - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *HMG | ||
| - | [[ | + | **[[2mrc]] – HMG residues 17-99 – ''Plasmodium falciparum'' - NMR <br /> |
| - | + | }} | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of high mobility group protein (HMG)
Updated on 26-August-2025
References
- ↑ Bianchi ME, Manfredi AA. High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein at the crossroads between innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev. 2007 Dec;220:35-46. PMID:17979838 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-065X.2007.00574.x
- ↑ Fedele M, Battista S, Manfioletti G, Croce CM, Giancotti V, Fusco A. Role of the high mobility group A proteins in human lipomas. Carcinogenesis. 2001 Oct;22(10):1583-91. PMID:11576996
- ↑ Tang D, Kang R, Zeh HJ 3rd, Lotze MT. High-mobility group box 1 and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Jan-Feb;1799(1-2):131-40. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2009.11.014. PMID:20123075 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2009.11.014