1ext
From Proteopedia
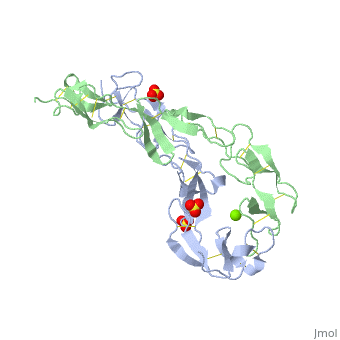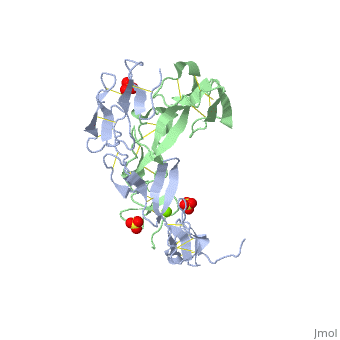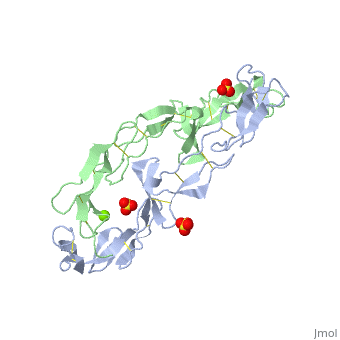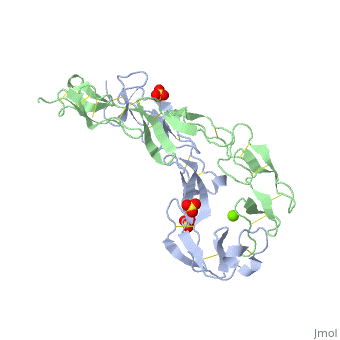
EXTRACELLULAR DOMAIN OF THE 55KDA TUMOR NECROSIS FACTOR RECEPTOR. CRYSTALLIZED AT PH3.7 IN P 21 21 21.
Structural highlights
DiseaseTNR1A_HUMAN Defects in TNFRSF1A are the cause of familial hibernian fever (FHF) [MIM:142680; also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). FHF is a hereditary periodic fever syndrome characterized by recurrent fever, abdominal pain, localized tender skin lesions and myalgia. Reactive amyloidosis is the main complication and occurs in 25% of cases.[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] Genetic variation in TNFRSF1A is associated with susceptibility to multiple sclerosis 5 (MS5) [MIM:614810. A multifactorial, inflammatory, demyelinating disease of the central nervous system. Sclerotic lesions are characterized by perivascular infiltration of monocytes and lymphocytes and appear as indurated areas in pathologic specimens (sclerosis in plaques). The pathological mechanism is regarded as an autoimmune attack of the myelin sheat, mediated by both cellular and humoral immunity. Clinical manifestations include visual loss, extra-ocular movement disorders, paresthesias, loss of sensation, weakness, dysarthria, spasticity, ataxia and bladder dysfunction. Genetic and environmental factors influence susceptibility to the disease. Note=An intronic mutation affecting alternative splicing and skipping of exon 6 directs increased expression of isoform 4 a transcript encoding a C-terminally truncated protein which is secreted and may function as a TNF antagonist.[6] FunctionTNR1A_HUMAN Receptor for TNFSF2/TNF-alpha and homotrimeric TNFSF1/lymphotoxin-alpha. The adapter molecule FADD recruits caspase-8 to the activated receptor. The resulting death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) performs caspase-8 proteolytic activation which initiates the subsequent cascade of caspases (aspartate-specific cysteine proteases) mediating apoptosis. Contributes to the induction of non-cytocidal TNF effects including anti-viral state and activation of the acid sphingomyelinase. Evolutionary ConservationCheck, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedBACKGROUND: Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a powerful cytokine that is involved in immune and pro-inflammatory responses. Two TNF receptors that belong to the cysteine-rich low affinity nerve growth factor receptor family (TNF-R1 and TNF-R2) are the sole mediators of TNF signalling. Signalling is thought to occur when a trimer of TNF binds to the extracellular domains of two or three receptor molecules, which permits aggregation and activation of the cytoplasmic domains. The complex is then internalized within an endocytic vesicle, whereupon it dissociates at low pH. Structure of the soluble extracellular domain of the receptor (sTNF-R1) both in the unliganded and TNF-bound state have previously been determined. In both instances, the fourth subdomain of the receptor was found to be partly disordered. In the unliganded state at pH 7.5, the extracellular domain forms two distinct types of dimer, parallel and antiparallel; the antiparallel dimer occludes the TNF-binding. RESULTS: We have determined the structure of sTNF-R1 in two crystal forms in high salt at pH 3.7. The orthorhombic crystals diffract to 1.85 and the entire polypeptide is well ordered. In contrast, the C-terminal 32 residues are disordered in the hexagonal crystals. In the orthorhombic form, these residues exhibit a topology and disulphide connectivity that differs from the other three cysteine-rich domains in the molecule. In both forms, the interface is considerably more extensive than that used in complex formation with LTalpha. This 'low pH' dimer is different from both of the dimers observed in crystals grown at pH 7.5. CONCLUSIONS: The occurrence of the antiparallel dimers in both low pH crystal forms suggest that they are not an artefact of crystal packing. Such dimers may form in the low pH environment of the endosome. Because the dimer contact surface occludes the TNF-binding site, formation of this dimer would dissociate the TNF-receptor complex within the endosome. Three of the four cysteine-rich domains of TNF-R1 are constructed from two distinct structural modules, termed A1 and B2. The fourth subdomain comprises an A1 module followed by an unusual C2 module. Although the orientation of these modules with respect to each other is sensitive to crystal packing, ligand binding, pH and ionic strength, the modules are structurally well conserved between and within the known sTNF-R1 structures. Structures of the extracellular domain of the type I tumor necrosis factor receptor.,Naismith JH, Devine TQ, Kohno T, Sprang SR Structure. 1996 Nov 15;4(11):1251-62. PMID:8939750[7] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
| ||||||||||||||||||||