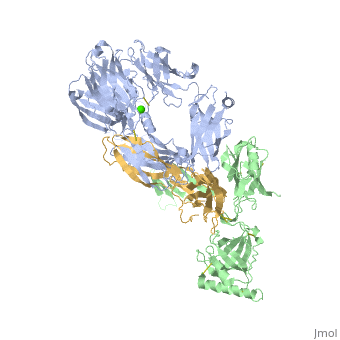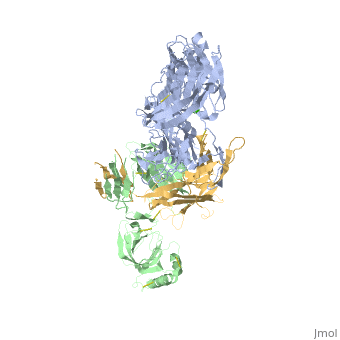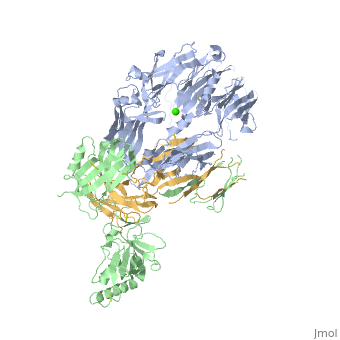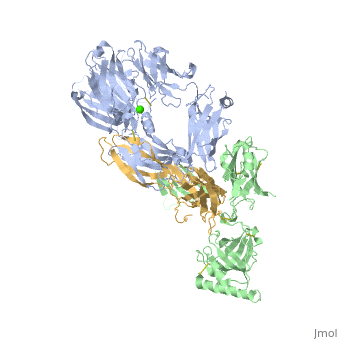
Structural highlights
Function
VCO3_NAJKA Complement-activating protein in cobra venom. It is a structural and functional analog of complement component C3b, the activated form of C3. It binds factor B (CFB), which is subsequently cleaved by factor D (CFD) to form the bimolecular complex CVF/Bb. CVF/Bb is a C3/C5 convertase that cleaves both complement components C3 and C5. Structurally, it resembles the C3b degradation product C3c, which is not able to form a C3/C5 convertase. Unlike C3b/Bb, CVF/Bb is a stable complex and completely resistant to the actions of complement regulatory factors H (CFH) and I (CFI). Therefore, CVF continuously activates complement resulting in the depletion of complement activity.
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
Cobra venom factor (CVF) is a functional analog of human complement component C3b, the active fragment of C3. Similar to C3b, in human and mammalian serum, CVF binds factor B, which is then cleaved by factor D, giving rise to the CVFBb complex that targets the same scissile bond in C3 as the authentic complement convertases C4bC2a and C3bBb. Unlike the latter, CVFBb is a stable complex and an efficient C5 convertase. We solved the crystal structure of CVF, isolated from Naja naja kouthia venom, at 2.6 A resolution. The CVF crystal structure, an intermediate between C3b and C3c, lacks the TED domain and has the CUB domain in an identical position to that seen in C3b. The similarly positioned CUB and slightly displaced C345c domains of CVF could play a vital role in the formation of C3 convertases by providing important primary binding sites for factor B.
The crystal structure of cobra venom factor, a cofactor for C3- and C5-convertase CVFBb.,Krishnan V, Ponnuraj K, Xu Y, Macon K, Volanakis JE, Narayana SV Structure. 2009 Apr 15;17(4):611-9. PMID:19368894[1]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Krishnan V, Ponnuraj K, Xu Y, Macon K, Volanakis JE, Narayana SV. The crystal structure of cobra venom factor, a cofactor for C3- and C5-convertase CVFBb. Structure. 2009 Apr 15;17(4):611-9. PMID:19368894 doi:10.1016/j.str.2009.01.015