We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
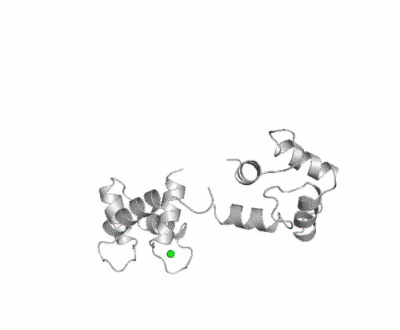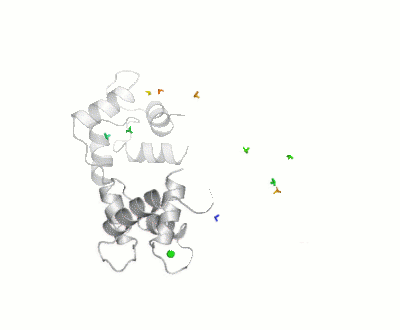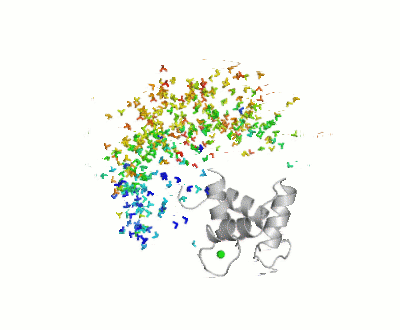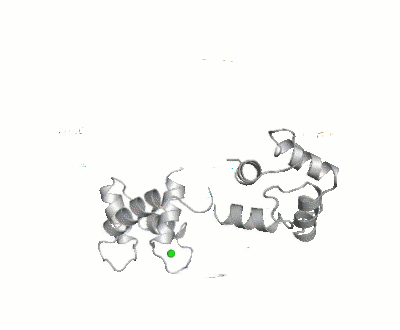
Calmodulin
From Proteopedia
| |||||||||||
See Also
Bibliography
- ↑ Chattopadhyaya R, Meador WE, Means AR, Quiocho FA. Calmodulin structure refined at 1.7 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 20;228(4):1177-92. PMID:1474585
- ↑ Bertini I, Giachetti A, Luchinat C, Parigi G, Petoukhov MV, Pierattelli R, Ravera E, Svergun DI. Conformational Space of Flexible Biological Macromolecules from Average Data. J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Sep 7. PMID:20822180 doi:10.1021/ja1063923
- ↑ The Storymorph Jmol scripts creates the interpolated coordinates of the morph on the fly.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Karsten Theis, Jaime Prilusky, Enrico Ravera, Daniel Moyano-Marino