Function
Calreticulin (CALR) is a multifunction calcium-binding chaperone. CALR is a molecular chaperone, an extracellular lectin, an intracellular mediator of integrin function, an inhibitor of steroid hormone-regulated gene expression and a C1q-binding protein[1].
Disease
Most patients with essential thrombocythemia or primary myelofibrosis not associated with JAK2 or MPL mutation have CALR mutation[2].
Relevance
CALR is active in regulating intracellular Ca+2 homeostasis[3].
Structural highlights
: N-terminal globular domain which has chaperone function; P-domain which is proline-rich, binds Ca+2 with high affinity and possesses a lectin-like chaperone function; C-terminal domain containing an ER retention signal.
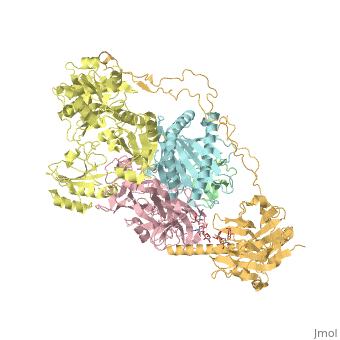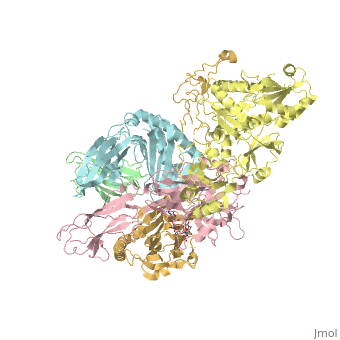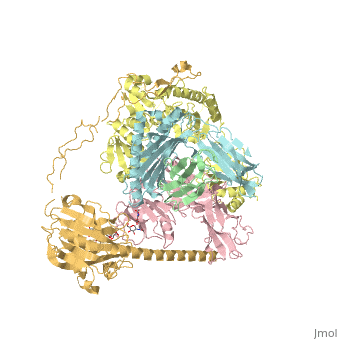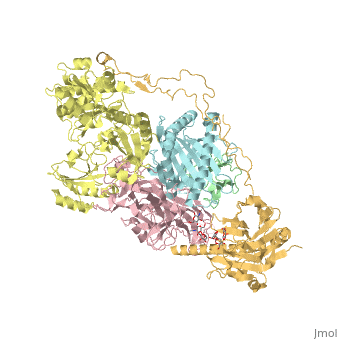
3D Structures of calreticulin
Calreticulin 3D structures