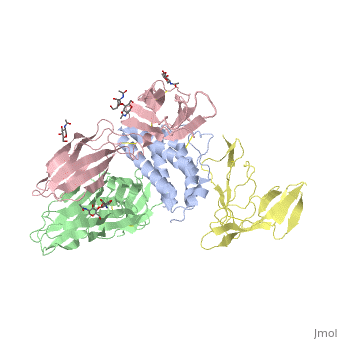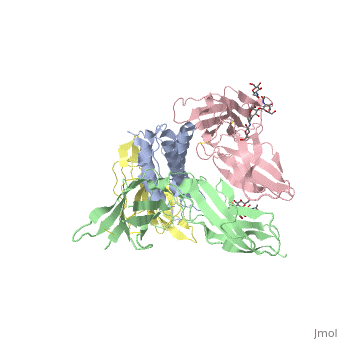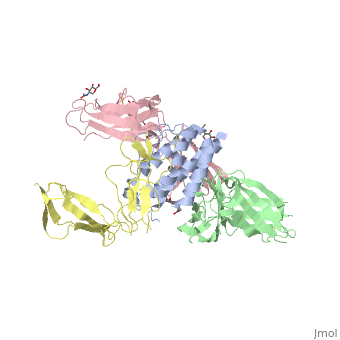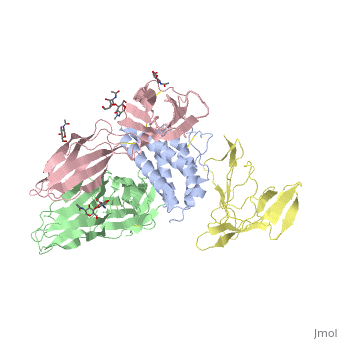Function
Interleukin receptors (ILR) are cytokine receptors belonging to the ILR of immunoglobulin family. which are classified into type I, type II and others.
- ILR type I are cell surface receptors which recognize cytokines with four α-helical strand. binding interleukin-1 (IL1) transmitting its inflammatory effect.
- ILR type II are similar to type I but lack the former’s signature sequence: WXSWS. They suppresses IL1 activity. Another suppressor of IL1R activity is the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL1R1A).
See also: Cytokine receptors.
TYPE-1 INTERLEUKIN-1 RECEPTOR COMPLEXED WITH INTERLEUKIN-1 BETA
Interleukin-1 receptor complex with ligand and go through the plasma membrane. 3D structure is showing here. Ribbon diagram of s-IL 1R complex to IL-1β. The complex has approximate dimensions of 97Å × 52Å ×35Å with one s-IL1R molecule wrapping around the IL-1β molecule with 1:1 ratio. In the , domain 3 provides a 'lid' which covers most of the top of the IL-1β β-barrel, whereas domains 1 and 2 from a groove which binds to the lower rim of the barrel. Here, Domains 1,2 and 3 of s-IL 1R are colored light, medium and dark blue, respectively. IL-1β is yellow, with site A residues in green and site B residues in red. The structure is oriented so that the carboxy terminus of s-IL 1R and the cell membrane are at the bottom of the picture.
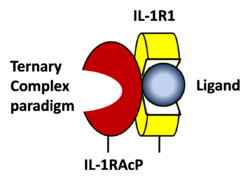
STRUCTURE OF THE INTERLEUKIN-1BETA SIGNALING COMPLEX
3D structure was showed here, and the cartoon (right) showed the formation of the ternary complex paradigm, the primary receptors (IL-1R) first bind their corresponding cytokine ligands (IL-1β) and then engage the accessory receptor (IL-1RAcP) (which is incapable of binding cytokines by itself). The overall ternary architecture of the IL-1β–IL-1RI–IL-1RAcP signaling complex has the cytoplasmic TIR domain necessary for signal transduction. The IL-1RI-IL-1RAcP interface was most hydrogen-bonded and signal was transferred through the highly packed hydrophobic region between receptor accessory and IL-1R liganded with IL-1β.
The dimer complex with conserved area was showed when you . The insert are ligands (IL-1β), which are present as conserved structure as well as green ribbon. The two IL-1Rs and two IL-1RAcPs are colored as purple and blue, respectively.
Clinical significance
Why are people interested in IL-1? Because IL-1 cytokines family are usually over-expressed at tumor sites or inflammatory, these cytokines could be used as bio-markers to help diagnose in advance. Also, since IL-1α, IL-1β and IL-1ra all have the ability to bind to the type 1 IL-1 receptor (IL-1R), and the binding of IL-1α or IL-1β to IL-1R is an early step in IL-1 signal transduction, blocking this interaction may therefore be a useful target for the development of new drugs.
See also:
3D structures of interleukin receptor
Interleukin receptor 3D structures