Fluoride inhibition of Sporosarcina pasteurii urease: structure and thermodynamics
Stefano Benini, Michele Cianci, Luca Mazzei and Stefano Ciurli [1]
Molecular Tour
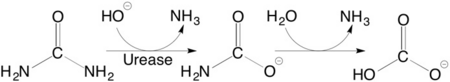
(it is in homotrimeric form of αβγ heterotrimer) is a nickel-dependent enzyme (Ni(II) ions are shown as green spheres, α, β, and γ subunits are colored in darkmagenta, yellow, deeppink, respectively) and a virulence factor for ureolytic bacterial human pathogens, but it is also necessary to convert urea (see static image below), the most worldwide used fertiliser, into forms of nitrogen that can be taken up by crop plants.
A strategy to control the activity of urease for medical and agricultural applications is to use enzyme inhibitors. Fluoride is a known urease inhibitor, but the structural basis of its mode of inhibition are still undetermined. Here, kinetic studies on the fluoride-induced inhibition of urease from Sporosarcina pasteurii, a widespread and highly ureolytic soil bacterium, revealed a mixed competitive and uncompetitive mechanism. The pH-dependence of the inhibition constants, investigated in the 6.5-8.0 range, reveals a predominant uncompetitive mechanism that increases by increasing the pH, and a lesser competitive inhibition that increases by lowering the pH. Ten crystal structures of the enzyme were independently determined using five crystals of the and five crystals of the protein crystallised in the presence of fluoride. The analysis of these structures revealed the presence of , in terminal and bridging positions (both fluorides are colored in gold). .
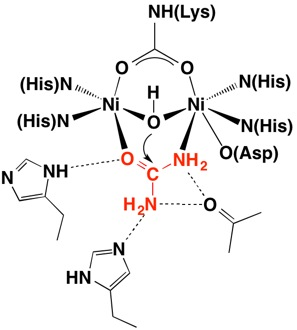
Structural studies on ureases have revealed that the immediate environment around the two Ni(II) ions at the active site is conserved, as to induce a common mechanism of catalysis whose key step is the nucleophilic attack of the nickel-bridging hydroxide on the urea molecule bound to the bimetallic nickel cluster via O and N atoms (see static image below).
The present study consistently supports an interaction of fluoride with the nickel centres in the urease active site in which (colored in salmon) to the Ni(II) ion proposed to coordinate urea in the initial step of the catalytic mechanism, while (colored in cyan) the Ni(II)-bridging hydroxide, blocking its nucleophilic attack on urea.
PDB references: 1.58 A resolution native Sporosarcina pasteurii urease 4ceu; 1.59 A resolution Fluoride inhibited Sporosarcina pasteurii urease 4cex.