We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
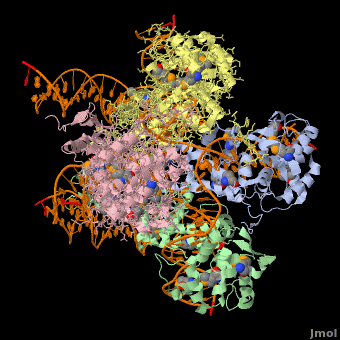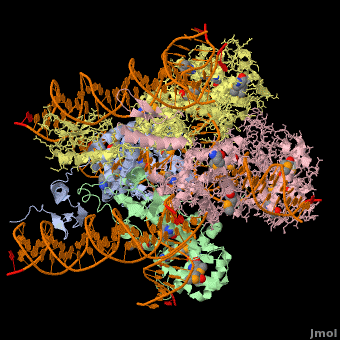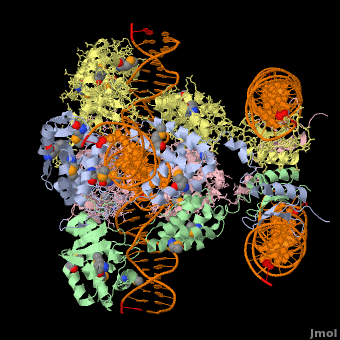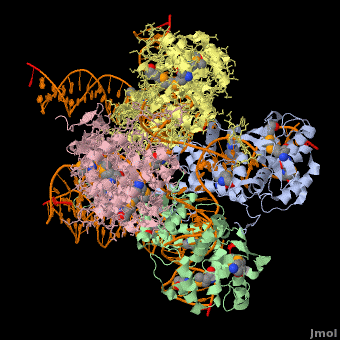
Phage integrase
From Proteopedia
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of phage integrase see Retroviral Integrase
References
- ↑ Groth AC, Calos MP. Phage integrases: biology and applications. J Mol Biol. 2004 Jan 16;335(3):667-78. PMID:14687564 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0022283603013561