Free Modeling Results
More than 100 domains were provided as prediction targets in CASP 14. 14 of these were in the most difficult category, free modeling ("FM"), meaning that no informative homology modeling templates existed. For 8 of these (57%), AlphaFold2's predictions achieved GDT_TS scores of 87-93 (median 88.5). For those 8, GDT_TS of the second best predictions were 43-76 (median 66). Two cases will be analyzed below.
First, SARS-CoV-2 ORF8[2], a 92-residue FM domain where AlphaFold2's GDT_TS was 87, and the second best was 43 (by the group of Xian Ming Pan)[3], the largest difference between 1st and 2nd predictions among the FM targets. It is further unusual because two independently-determined X-ray crystallographic structures were subsequently published. Inspiration for this case came from the discussion by Rubiera[4].
Second, the longest domain in the FM category, 404 residues. This domain is part of the 2,180-residue RNA polymerase of a bacteriophage, some of whose group members are prevalent in the human gut[5]. Eight of the CASP 14 FM target domains are parts of this protein, 6vr4. For the 404-residue domain, AlphaFold2 achieved GDT_TS of 88, and the second best prediction, 63 (by Seok-refine). Among the 14 FM targets, the second-longest has 276 residues, the median 132, and the shortest, 92.
SARS-CoV-2 ORF8
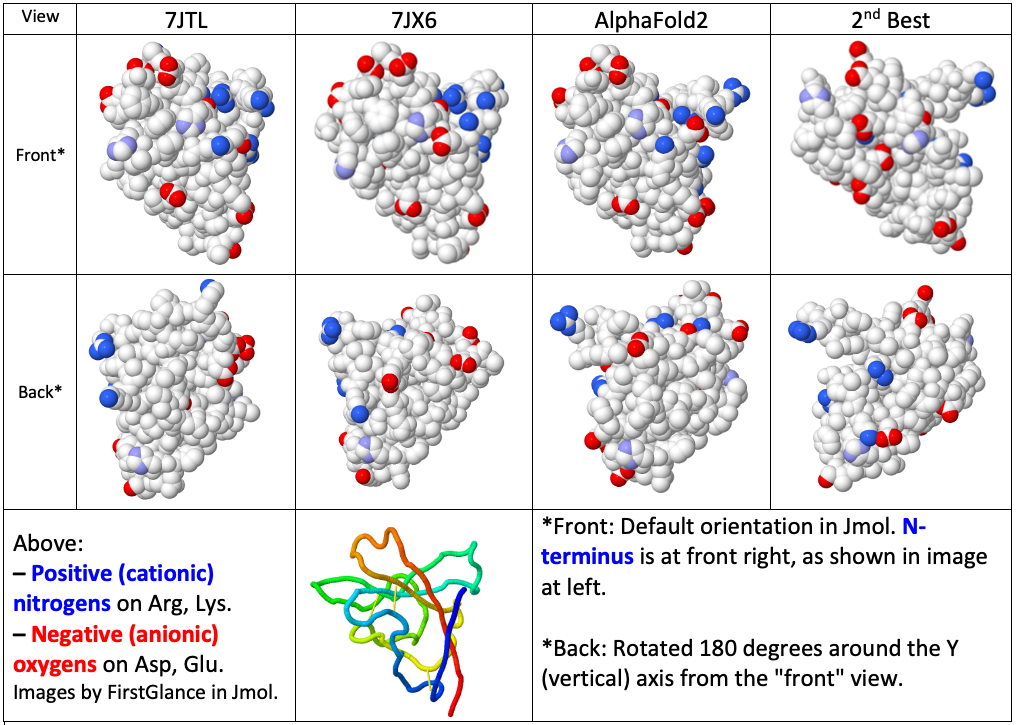
Our first example is SARS-CoV-2 protein ORF8, a protein that contributes to virulence in COVID-19[2]. CASP 14 classified ORF8 as a "free modeling" (FM) target[6], meaning that there were no adequate empirical templates for homology modeling. This was easily confirmed. When the amino acid sequence of ORF8 is submitted to Swiss Model, it reports the best templates for homology modeling. When the two empirical models that were not available during CASP 14 are excluded (7jtl and 7jx6), the best template offered, chain B of 3afc, covers only 36% of the length of ORF8 at 13.2% sequence identity, with a 4-residue untemplated gap in the sequence alignment. This template would not be adequate for constructing a useful model.
X-Ray Structures for ORF8
The quality of predictions for the structure of ORF8 are judged by comparison with X-ray crystallographic empirical models which were not available to the groups making predictions. Shortly after the CASP 14 competition (summer 2020), two X-ray crystal structures were reported for ORF8: 7jtl released August 26, 2020, and 7jx6, released September 23, 2020. The resolutions are 2.0 and 1.6 Å respectively, and both have worse than average Rfree values.
Click the green links below to change the molecular scene. Drag to rotate.
Zoom the molecule with your mouse wheel, or Shift-Drag up/down.
|
from the higher resolution X-ray structure, 7jx6. These chains form disulfide-linked dimers, and the dimers form higher order multimers[2] (not shown). Notice that the amino and carboxy ends of the chain come together to form two parallel beta strands of a beta sheet. Also notice that there are 3 disulfide bonds. An accurate prediction would include both of these features.
[7]. The only substantial disagreement is for a large surface loop, sequence range 48-57. See the Table I below for RMSD values.
ORF8 is not a novel fold
Less than 2% of new empirically-determined structures have novel folds; that is, folds not aready represented in the PDB[8]. When chain A of 7jx6 was submitted to Dali[9] (February, 2021), the top hit was the N-terminal domain of the two domains in 5a2f, the CD166 human cell surface receptor involved in activation of T lymphocytes. The Z-score was 7.1, and 88 alpha carbons superposed with RMSD 3.2 Å. Swiss-PdbViewer obtained RMSD 1.95 Å for 48 alpha carbons[10]. Dali reported the identity as 6% in its structure-based sequence alignment. Sequence alignment by MAFFT[11] obtained 18% sequence identity using more and larger gaps. [12] is not as close as for AlphaFold2's prediction, but is closer than the 2nd best prediction (see Table I below). In conclusion, ORF8 does not have a novel fold[13].
AlphaFold2 Prediction for ORF8
The quality of a prediction in CASP is judged, in large part, by the Global Distance Test Total Score, GDT_TS. AlphaFold2's predicted structure[14] has a GDT_TS score of 87. (A score of 0 is meaningless, and a score of 100 means perfect agreement with an X-ray crystal structure.) 87 means [7]. The structure predicted by AlphaFold2 is almost as close to the X-ray crystallographic model 7jx6 as is the independently-determined X-ray structure 7jtl. AlphaFold2 predicted the positions of 92 amino acids. (CASP 14 excluded residues 48-59, a 12-residue surface loop, from the target residues[6].) See Table I below for RMSD values. The prediction was largely accurate regarding salt bridges and cation-pi interactions (see Tables II and III below).
Table I. ORF8 Predictions Superposed With Chain A of 7jx6
| Model | GDT_TS | Disulfde
Bonds | Cα RMSD, Å | Cα Superposed | RMSD Including
Sidechains, Å | Atoms Superposed
|
| 7jtl:A | 88[15] | 3 | 4.02
0.66 | 102/102 (100%)
87/102 (85%) | 4.3
1.58 | 829/829 (100%)
709/829 (86%)
|
| AlphaFold2 | 87 | 3 | 2.58
1.25 | 92/92 (100%)
83/92* (90%) | 3.23
1.91 | 747/748 (100%)
679/748 (91%)
|
| Dali top hit[16] 5a2f | 53[15] | na | 3.2
1.95 | 92/92 (100%)
48/92 (52%) | na | na
|
| 2nd Best* | 43 | 0 | 5.33
1.71 | 92/92 (100%)
38/92 (41%) | 6.54
5.86 | 747/748 (100%)
324/748 (43%)
|
| 3rd Best§ | 33 | 0 | 13.37
† | 92/92 (100%)
† | 14.50
† | 747/748 (100%)
†
|
Zhang-TBM
Server | 27 | 0 | 14.90
† | 92/92 (100%)
† | 15.61
† | 747/748 (100%)
†
|
Rosetta
Server | 26 | (2‡) | 14.99
† | 92/92 (100%)
† | 16.07
† | 747/748 (100%)
†
|
- Superpositions by "Magic Fit"[17] of Swiss-PdbViewer 4.1.
- Superpositions by "Iterative Magic Fit"[7] of Swiss-PdbViewer 4.1.
- na: Not Applicable.
- *Second best: Group of Xian Ming Pan, Tsinghua University, Beijing.
- §Third best: Group of Alberto Perez, University of Florida, Gainsville.
- † Iterative Magic Fit was unable to superpose.
- ‡ Neither disulfide bond is correct.
Second Best Prediction for ORF8
In CASP 14, 70 research groups and 42 automated servers predicted structures for ORF8. The median GDT_TS score for all 112 predictions was 26. AlphaFold2 made the best prediction (GDT_TS 87). [7], with GDT_TS 43 (see Table I above). The fold and topology were predicted correctly, but the details are far less accurate than those in AlphaFold2's prediction. The 2nd best prediction has no disulfide bonds. This prediction was largely incorrect regarding salt bridges and cation-pi interactions (see Tables II and III below).
Third Best Prediction for ORF8
The third best prediction for ORF8 was by the Perez Lab, with GDT_TS 33 (see Table I above). It correctly predicted the parallel beta strands formed by the amino and carboxy terminal ends of the chain. [18]. This prediction has no disulfide bonds. The salt bridge Arg86:Asp98 is correctly predicted, along with two incorrectly predicted salt bridges.
Top Prediction by an Automated Server
Among predictions by automated servers for all ~100 CASP 14 targets, the top ranking server was QUARK from the Yang Zhang group (Univ. Michigan). For ORF8, the Zhang-TBM server made the best server prediction with a GDT_TS of 27. (The prediction by QUARK was almost as good, GDT_TS 26.) The prediction has the two chain termini not parallel, and the amino terminus is not a beta strand, differing in both respects from the X-ray model. Also, no disulfide bonds are predicted. The salt bridge Arg86:Asp98 is correctly predicted, along with several incorrectly predicted salt bridges. The structural superposition is very poor and is not shown.
Baker Rosetta Server Prediction for ORF8
Among predictions for all ~100 CASP 14 targets, the group of David Baker ranked second. The Rosetta Server of the Baker group ranked 18th overall, but was the 4th ranked server[19]. For ORF8, the Rosetta Server prediction GDT_TS was 26, a bit better than the median of 23. The Rosetta Server's prediction for ORF8 has the two termini far apart (Cα 13 Å or farther apart), a substantial difference from the X-ray structure (Cα mostly ~5 Å apart). It predicts two disulfide bonds, but neither matches the pairs of Cys residues in the actual disulfide bonds. The salt bridge Arg86:Asp98 is correctly predicted, along with one incorrectly predicted salt bridge. The structural superposition is very poor and is not shown.
Phage RNA polymerase
Our second example is a 404-residue domain within a 2,180 residue RNA polymerase, 6vr4, gp66 from a bacteriophage of the crAss-like group, some members of which are prevalent in the human gut[5]. One host for the target-containing phage is gram-negative, aerobic bacteria Cellulphaga baltica isolated from marine microalga[20]. CASP 14 classified this domain, designated T1037, as a free modeling ("FM") target, meaning that no informative templates existed in the PDB.