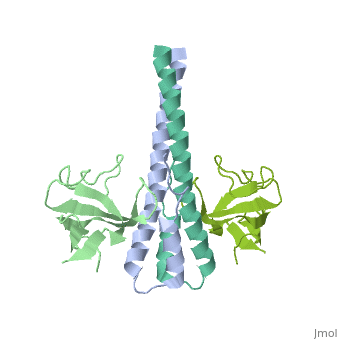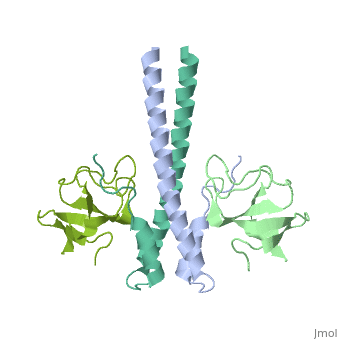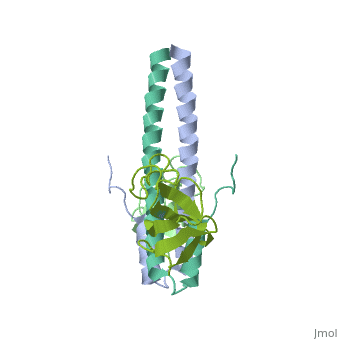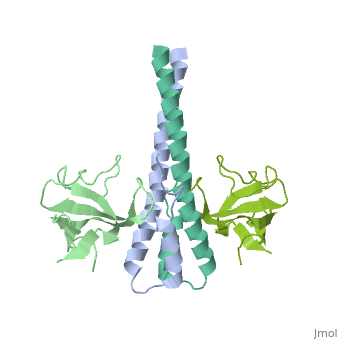
End-binding protein or telomere-binding protein or microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member (EB) regulates microtubules dynamics, promotes colony formation and enhances tumor growth. EB is part of the proteins which accumulate at the growing microtubule plus end. During mitosis the EB associates with centrosome and spindle microtubules. EB is involved in the regulation of chromosome stability and microtubule structure. The C terminal domains of EB1 and EB3 are involved in dimer formation. The CH (Calponin Homology) domain is an actin-binding domain[1].
- End-binding protein 1 accumulates at growing microtubule ends and regulates their dynamics[2].
- End-binding protein 2 is involved in initial microtubule reorganization promoting stability and bundle formation[3].