Solution structure and dynamics of human S100A14
Ivano Bertini, Valentina Borsi, Linda Cerofolini, Soumyasri Das Gupta, Marco Fragai and Claudio Luchinat [1]
Molecular Tour
Human is a member of the EF-hand calcium-binding protein family that has only recently been described in its functional and pathological properties. The protein is overexpressed in a variety of tumor cells and it has been shown to trigger receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE)-dependent signaling in cell cultures. The protein has a high degree of sequence homology with S100A13 although it exhibits a negligible affinity for calcium(II) ions and undergoes aggregation and precipitation in the presence of zinc(II) or copper(II) ions. The lack of two ligands in the canonical EF-hand calcium(II)-binding site explains the negligible affinity for calcium(II) in solution, while the exposed cysteines and histidine account for the observed precipitation in the presence of zinc(II) or copper(II) ions. in S100A13 as well as in other S100 proteins, are mutated in S100A14. The solution structure of (monomer A is in mediumslateblue and monomer B is in deeppink) in the apo state at physiological temperature shows close structural similarities with the C-terminal domain of the myosin light chains and folds in a ‘semi-open’ conformation, with helices III and IV showing a X-shaped offset arrangement and helices II and III showing a high number of interactions creating a V-shaped arrangement.
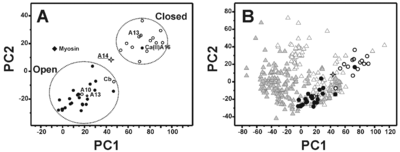
Principal component analysis performed on the six inter-helical angles of the apo and calcium(II)-loaded forms of S100 proteins. Apo and holo proteins are represented as open and filled circles, respectively. The two open circles not regularly placed with respect to the others correspond to the apo form of calbindin D9k (Cb) and S100A10 (A10). The filled circle placed in the region of protein in closed conformation corresponds to holo S100A16 (A16). S100A14 (open star) is in a ‘semi-open’ conformation in physiological conditions. Apo and holo form of S100A13 are reported as open and closed stars, respectively. Myosin light chain is reported as filled diamond. B). Principal component plot of the whole EFhD dataset derived from principal component analysis of the six inter-helix angles. Apo and holo proteins are represented as open and filled grey triangles, respectively. S100 proteins are reported with the same symbols as in A.
The interacting aromatic residues in stabilize the interhelical orientation
The most remarkable feature of this structural conformation involves the packing of the helices that is reduced with respect to the ‘closed’ structures of the S100 proteins but is still sizably larger than the corresponding ‘open’ structures. At the same time, the analysis of the electrostatic potential surface suggests that the is .
PDB reference: 2m0r.


