User:Ke Xiao/Geobacter pilus models
From Proteopedia
Interactive 3D Complement in Proteopedia
Scientific Reports an online, open access journal: nature.com/srep
Low energy atomic models suggesting a pilus structure that could account for electrical conductivity of Geobacter sulfurreducens pili.
Ke Xiao, Nikhil S. Malvankar, Chuanjun Shu, Eric Martz, Derek R. Lovley, and Xiao Sun.
Scientific Reports 6:23385, March 2016: nature.com/articles/srep23385. (DOI: 10.1038/srep23385)
|
CAVEAT: The theoretical model described here was published in 2016. In 2019, cryo-EM structures of highly conductive Geobacter nanowires were found to be composed of the cytochrome OmcS[1][2]. This called into question whether highly conductive pilus nanowires composed of the protein pilA exist. |
Molecular Tour
| |||||||||||
| Theoretical Model: The protein structure described on this page was determined theoretically, and hence should be interpreted with caution. |
Download
Pilus Model
- Click to download Geobacter sulfurreducens pilus model ARC-1
- Explore pilus model in FirstGlance in Jmol.
Animations for Powerpoint
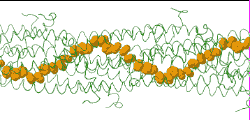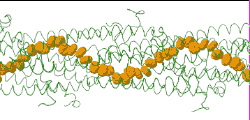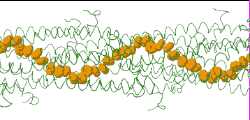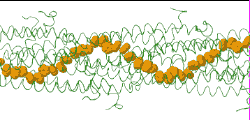
| Low resolution, ARC-1 model (smoothed green backbone traces) with aromatic rings of residues Phe1, Phe24, and Tyr27 in orange. DOWNLOAD HIGH RESOLUTION ANIMATION (19 MB). |
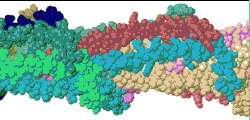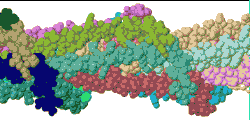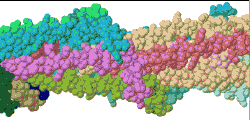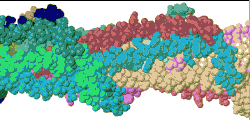
| Low resolution, ARC-1 model with spacefilling (van der Waals) atoms, each chain a different color. DOWNLOAD HIGH RESOLUTION ANIMATION (29 MB). |
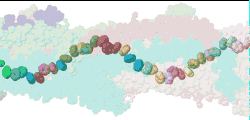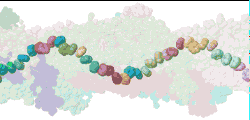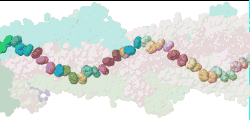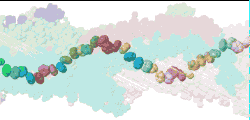
| Low resolution, ARC-1 model with translucent spacefilling atoms. Aromatic rings of Phe1, Phe24, and Tyr27 are opaque. Each chain is a different color. DOWNLOAD HIGH RESOLUTION ANIMATION (28 MB). |
See Also
Notes & References
- ↑ Wang F, Gu Y, O'Brien JP, Yi SM, Yalcin SE, Srikanth V, Shen C, Vu D, Ing NL, Hochbaum AI, Egelman EH, Malvankar NS. Structure of Microbial Nanowires Reveals Stacked Hemes that Transport Electrons over Micrometers. Cell. 2019 Apr 4;177(2):361-369.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.03.029. PMID:30951668 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.03.029
- ↑ Filman DJ, Marino SF, Ward JE, Yang L, Mester Z, Bullitt E, Lovley DR, Strauss M. Cryo-EM reveals the structural basis of long-range electron transport in a cytochrome-based bacterial nanowire. Commun Biol. 2019 Jun 19;2(1):219. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0448-9. PMID:31925024 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s42003-019-0448-9
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Xiao K, Malvankar NS, Shu C, Martz E, Lovley DR, Sun X. Low Energy Atomic Models Suggesting a Pilus Structure that could Account for Electrical Conductivity of Geobacter sulfurreducens Pili. Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 22;6:23385. doi: 10.1038/srep23385. PMID:27001169 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/srep23385
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Malvankar NS, Vargas M, Nevin K, Tremblay PL, Evans-Lutterodt K, Nykypanchuk D, Martz E, Tuominen MT, Lovley DR. Structural basis for metallic-like conductivity in microbial nanowires. MBio. 2015 Mar 3;6(2):e00084. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00084-15. PMID:25736881 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00084-15
- ↑ Craig L, Volkmann N, Arvai AS, Pique ME, Yeager M, Egelman EH, Tainer JA. Type IV pilus structure by cryo-electron microscopy and crystallography: implications for pilus assembly and functions. Mol Cell. 2006 Sep 1;23(5):651-62. PMID:16949362 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2006.07.004
- ↑ Craig L, Taylor RK, Pique ME, Adair BD, Arvai AS, Singh M, Lloyd SJ, Shin DS, Getzoff ED, Yeager M, Forest KT, Tainer JA. Type IV pilin structure and assembly: X-ray and EM analyses of Vibrio cholerae toxin-coregulated pilus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK pilin. Mol Cell. 2003 May;11(5):1139-50. PMID:12769840
- ↑ The chemical realism of these theoretical energy-minimized models contrasts with models where empirical monomer structures are docked into cryo-electron microscopic electron density maps. Those are unrealistic in details of subunit interactions, lacking shape complementarity and having many atomic clashes. See "Initial Model Outputs" in the publication for details.
- ↑ Each chain contains the 61 C-terminal amino acids of UniProt Q74D23.
- ↑ Campos M, Francetic O, Nilges M. Modeling pilus structures from sparse data. J Struct Biol. 2011 Mar;173(3):436-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2010.11.015. Epub 2010 , Nov 27. PMID:21115127 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2010.11.015
- ↑ Craig L, Pique ME, Tainer JA. Type IV pilus structure and bacterial pathogenicity. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004 May;2(5):363-78. PMID:15100690 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro885
- ↑ Li J, Egelman EH, Craig L. Structure of the Vibrio cholerae Type IVb Pilus and stability comparison with the Neisseria gonorrhoeae type IVa pilus. J Mol Biol. 2012 Apr 20;418(1-2):47-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.02.017. Epub 2012, Feb 21. PMID:22361030 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2012.02.017
- ↑ Craig L, Volkmann N, Arvai AS, Pique ME, Yeager M, Egelman EH, Tainer JA. Type IV pilus structure by cryo-electron microscopy and crystallography: implications for pilus assembly and functions. Mol Cell. 2006 Sep 1;23(5):651-62. PMID:16949362 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2006.07.004