Function
Endonuclease (ENN) cleaves phosphodiester bond within polynucleotide chain. ENN cleaves DNA at a restriction site which is usually a 6-nucleotide palindrome. ENN is restriction site–specific. Various types of ENN differ by their mechanism of action. ENN is used in genetic engineering to make recombinant DNA. ENN requires a restriction site and a cleavage pattern.
- ENN-I operates on DNA with separate restriction site and cleavage pattern.
- ENN-II operates on overlapping restriction site and cleavage pattern.
- ENN-III is a bifunctional DNA glycosylase that removes oxidized pyrimidines from DNA[1].
- ENN-IV cleaves the DNA backbone 5' of AP sites[2].
- ENN-V removes deaminated bases from DNA[3].
- ENN-VII recognizes mixmatches in DNA recombinational heteroduplexes and performs their incision[4].
- ENN-VIII removes radiolysis thymine products from phage DNA and cleaves the DNA at AP sites[5].
- Structure-specific ENN specific for DNA secondary structure rather than for its sequence[6].
- Intron-encoded ENN or homing ENN are encoded by genes with mobile, self-splicing introns. They promote the movement of DNA sequences from one chromosome location to another[7].
The Cas ENN proteins are part of CRISPR/Cas prokaryotic immune system which confers protection from foreign genetic elements like viruses. The CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspersed Short Palindromic Repeats) are DNA loci which are found in ca. 40% of the bacteria. The CRISPR/Cas system is being used lately as gene editing tool[8]. For more details see
See also
Relevance
Sickle cell anemia is caused by mutation in the recognition site of MstII ENN.
Disease
Mutation in UV-specific ENN causes Xeroderma pigmentosa. Mutations in tRNA-splicing ENN cause pontocerebellar hypoplasia.
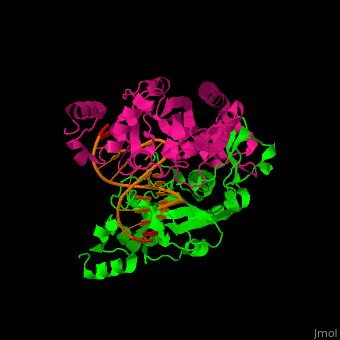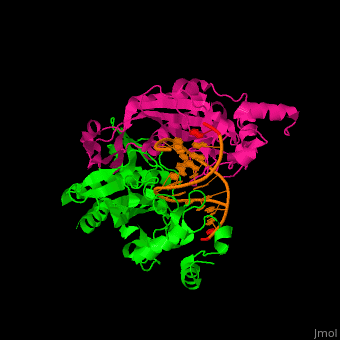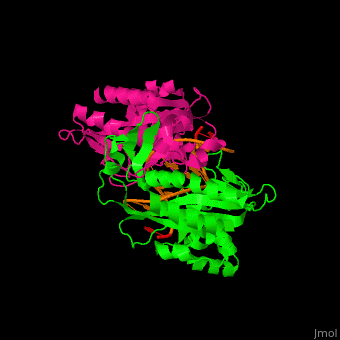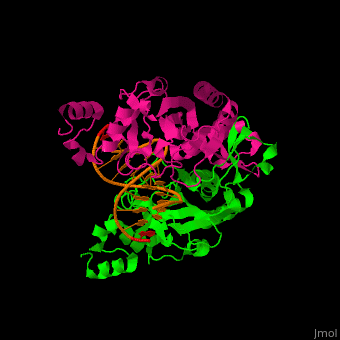
Structural highlights
(PDB code 1rva).
3D structures of endonuclease
Endonuclease 3D structures